Documentation for Substance Designer 3D is now available on Experience League. After March 14th, HelpX pages will automatically redirect to the equivalent Experience League page.
Refer to the FAQ for more information about which documentation is affected.
- Substance 3D home
- User guide
- Glossary
- Getting started
- Workspace
- Workspace
- Customizing your workspace
- Home screen
- Main toolbar
- Preferences
- Explorer
- Graph view
- Library
- Properties
- 2D view
- 3D view
- Dependency manager
- Resources
- Resources
- Importing, linking and new resources
- Bitmap resource
- Vector graphics (SVG) resource
- 3D scene resource
- AxF (Appearance eXchange Format)
- Font resource
- Warnings from dependencies
- Substance graphs
- Substance graphs
- Substance graph key concepts
- Creating a Substance graph
- Instances and subgraphs
- Graph parameters
- Manage parameters
- 'Visible if' expressions
- Inheritance in Substance graphs
- Output size
- Values in Substance graphs
- Publishing Substance 3D asset files (SBSAR)
- Exporting bitmaps
- Exporting PSD files
- Sample Substance graphs
- Warnings in Substance graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance graphs
- Atomic nodes
- Node library
- Node library
- Texture generators
- Texture generators
- Noises
- Noises
- 3D Perlin noise
- 3D Perlin noise fractal
- 3D Ridged noise fractal
- 3D Simplex noise
- 3D Voronoi
- 3D Voronoi fractal
- 3D Worley noise
- Anisotropic noise
- Blue noise fast
- BnW spots 1
- BnW spots 2
- BnW spots 3
- Cells 1
- Cells 2
- Cells 3
- Cells 4
- Clouds 1
- Clouds 2
- Clouds 3
- Creased
- Crystal 1
- Crystal 2
- Directional noise 1
- Directional noise 2
- Directional noise 3
- Directional noise 4
- Directional scratches
- Dirt 1
- Dirt 2
- Dirt 3
- Dirt 4
- Dirt 5
- Dirt gradient
- Fluid
- Fractal sum 1
- Fractal sum 2
- Fractal sum 3
- Fractal sum 4
- Fractal sum base
- Fur 1
- Fur 2
- Fur 3
- Gaussian noise
- Gaussian spots 1
- Gaussian spots 2
- Grunge concrete
- Grunge Damas
- Grunge galvanic large
- Grunge galvanic small
- Grunge leaks
- Grunge leaky paint
- Grunge map 001
- Grunge map 002
- Grunge map 003
- Grunge map 004
- Grunge map 005
- Grunge map 006
- Grunge map 007
- Grunge map 008
- Grunge map 009
- Grunge map 010
- Grunge map 011
- Grunge map 012
- Grunge map 013
- Grunge map 014
- Grunge map 015
- Grunge rough dirty
- Grunge rust fine
- Grunge scratches dirty
- Grunge scratches fine
- Grunge scratches rough
- Grunge shavings
- Grunge splashes dusty
- Grunge spots
- Grunge spots dirty
- Liquid
- Messy fibers 1
- Messy fibers 2
- Messy fibers 3
- Microscope view
- Moisture noise 1
- Moisture noise 2
- Perlin noise
- Plasma
- Caustics
- Voronoi
- Voronoi fractal
- Waveform 1
- White noise
- White noise fast
- Patterns
- Patterns
- 3D linear gradient
- 3D volume mask
- Alveolus
- Arc pavement
- Brick 1
- Brick 2
- Brick generator
- Checker 1
- Cube 3D
- Cube 3D GBuffers
- Fibers 1
- Fibers 2
- Gaussian 1
- Gaussian 2
- Gradient axial
- Gradient axial reflected
- Gradient circular
- Gradient linear 1
- Gradient linear 2
- Gradient linear 3
- Gradient radial
- Height extrude
- Mesh 1
- Mesh 2
- Panorama shape
- Polygon 1
- Polygon 2
- Scratches generator
- Shape
- Shape extrude
- Shape mapper
- Shape splatter
- Shape splatter blend
- Shape splatter data extract
- Shape splatter to mask
- Splatter
- Splatter circular
- Star
- Starburst
- Stripes
- Tile generator
- Tile random
- Tile random 2
- Tile sampler
- Triangle grid
- Weave 1
- Weave 2
- Weave generator
- Filters
- Filters
- Adjustments
- Adjustments
- Apply color palette
- Auto levels
- Channel mixer
- Chrominance extract
- Clamp
- Color match
- Color to mask
- Contrast/Luminosity
- Convert to linear
- Convert to sRGB
- Create color palette (16)
- Grayscale conversion advanced
- Hald CLUT
- HDR range viewer
- Height map frequencies mapper
- Highpass
- Histogram compute
- Histogram equalize
- Histogram range
- Histogram render
- Histogram scan
- Non-uniform histogram scan
- Histogram select
- Histogram shift
- ID to mask grayscale
- Invert
- Lighting cancel high frequencies
- Lighting cancel low frequencies
- Luminance highpass
- Min max
- Modify color palette
- Pow
- Quantize color (Simple)
- Quantize color
- Quantize grayscale
- Replace color
- Replace color range
- Threshold
- View color palette
- Blending
- Blurs
- Channels
- Effects
- Effects
- 3D texture position
- 3D texture SDF
- 3D texture surface render
- 3D texture volume render
- Ambient occlusion (HBAO)
- Ambient occlusion (RTAO)
- Anisotropic Kuwahara color
- Anisotropic Kuwahara grayscale
- Bevel
- Bevel smooth
- Cross section
- Curvature
- Curvature smooth
- Curvature sobel
- Diffusion color
- Diffusion grayscale
- Diffusion UV
- Directional distance
- Edge detect
- Emboss with gloss
- Extend shape
- Flood fill
- Flood fill mapper
- Flood fill to Bbox size
- Flood Fill to gradient
- Flood Fill to grayscale/color
- Flood Fill to index
- Flood Fill to position
- Flood Fill to random color
- Flood Fill to random grayscale
- FXAA
- Glow
- Mosaic
- Multi directional warp
- Non-uniform directional warp
- Reaction diffusion fast
- RT irradiance
- RT shadow
- Shadows
- Shape drop shadow
- Shape glow
- Shape stroke
- Summed area table
- Swirl
- Uber emboss
- Vector morph
- Vector warp
- Normal map
- Tiling
- Transforms
- Material filters
- Material filters
- 1-click
- Effects (Material)
- Transforms (Material)
- Blending (Material)
- PBR utilities
- Scan processing
- Mesh-based generators
- Mesh-based generators
- Mask generators
- Weathering
- Utilities (Mesh-based generators)
- Spline & Path tools
- Spline & Path tools
- Working with Path & Spline tools
- Paths to spline
- Path tools
- Spline tools
- Spline tools
- Point list
- Scatter on Spline color
- Scatter on Spline grayscale
- Scatter Splines on Splines
- Spline 2D transform
- Spline (Cubic)
- Spline (Poly quadratic)
- Spline (Quadratic)
- Spline append
- Spline bridge (2 Splines)
- Spline bridge (List)
- Spline bridge mapper color
- Spline bridge mapper grayscale
- Spline circle
- Spline fill
- Spline flow mapper
- Spline mapper color
- Spline mapper grayscale
- Spline merge list
- Spline render
- Spline sample height
- Spline sample thickness
- Spline select
- Spline warp
- UV mapper color
- UV mapper grayscale
- 3D view (Library)
- 3D view (Library)
- HDRI tools
- Node library
- Substance function graphs
- Substance function graphs
- What is a Substance function graph?
- Create and edit a function
- The Substance function graph
- Variables
- FX-maps
- FX-Maps
- How it works
- The Iterate node
- The Quadrant node
- Using Substance function graphs in FX-Maps
- Warnings in Substance function graphs
- Sample Substance function graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance function graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance function graphs
- Function nodes overview
- Atomic function nodes
- Function node library
- MDL graphs
- Working with 3D scenes
- Bakers
- Best practices
- Pipeline and project configuration
- Color management
- Package metadata
- Scripting
- Scripting
- Plugin basics
- Plugin search paths
- Plugins packages
- Plugin manager
- Python editor
- Accessing graphs and selections
- Nodes and properties
- Undo and redo
- Application callbacks
- Creating user interface elements
- Adding actions to the Explorer toolbar
- Using color management
- Using spot colors
- Logging
- Using threads
- Debugging plugins using Visual Studio Code
- Porting previous plugins
- Packaging plugins
- Scripting API reference
- Technical issues
- Release notes
Inheritance in Substance graphs
This page describes how inheritance is applied in Substance graphs within Substance 3D Designer, and the impact it has on the graph's output.
In this page


Overview
All nodes in a Substance graph can inherit the value of some parameters from a source. Inheritance means that changing the value in the source will carry out that change across all nodes which inherit from it. This is one of the fundamental concepts underpinning Substance 3D Designer’s power in generating parametric assets.
An annotated project file demonstrating inheritance is available in the Sample Substance graphs section of this documentation.
Inheritance methods


Absolute
No inheritance, the value is defined arbitrarily and locally for the parameter


Relative to input
The value is inherited from the data connected to the Primary input of the node


Relative to parent
The value is inherited from the parent of the node or graph
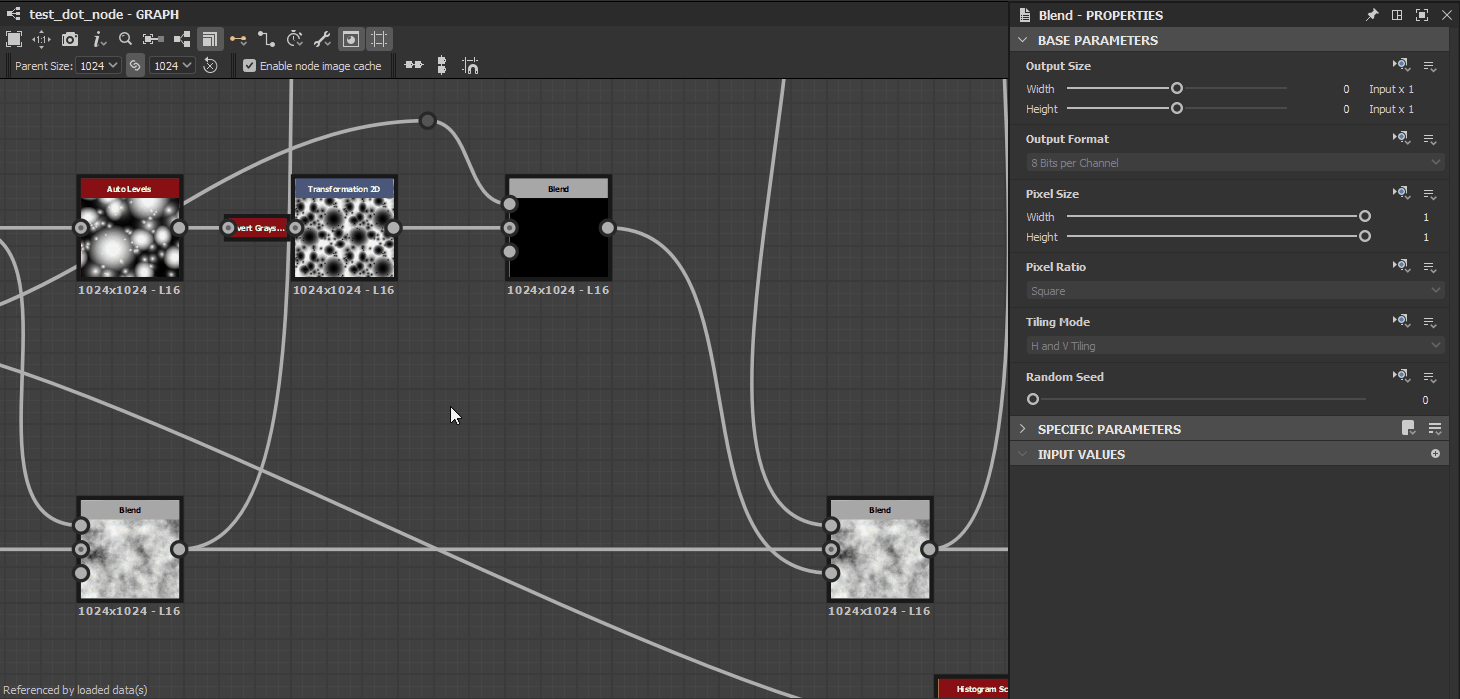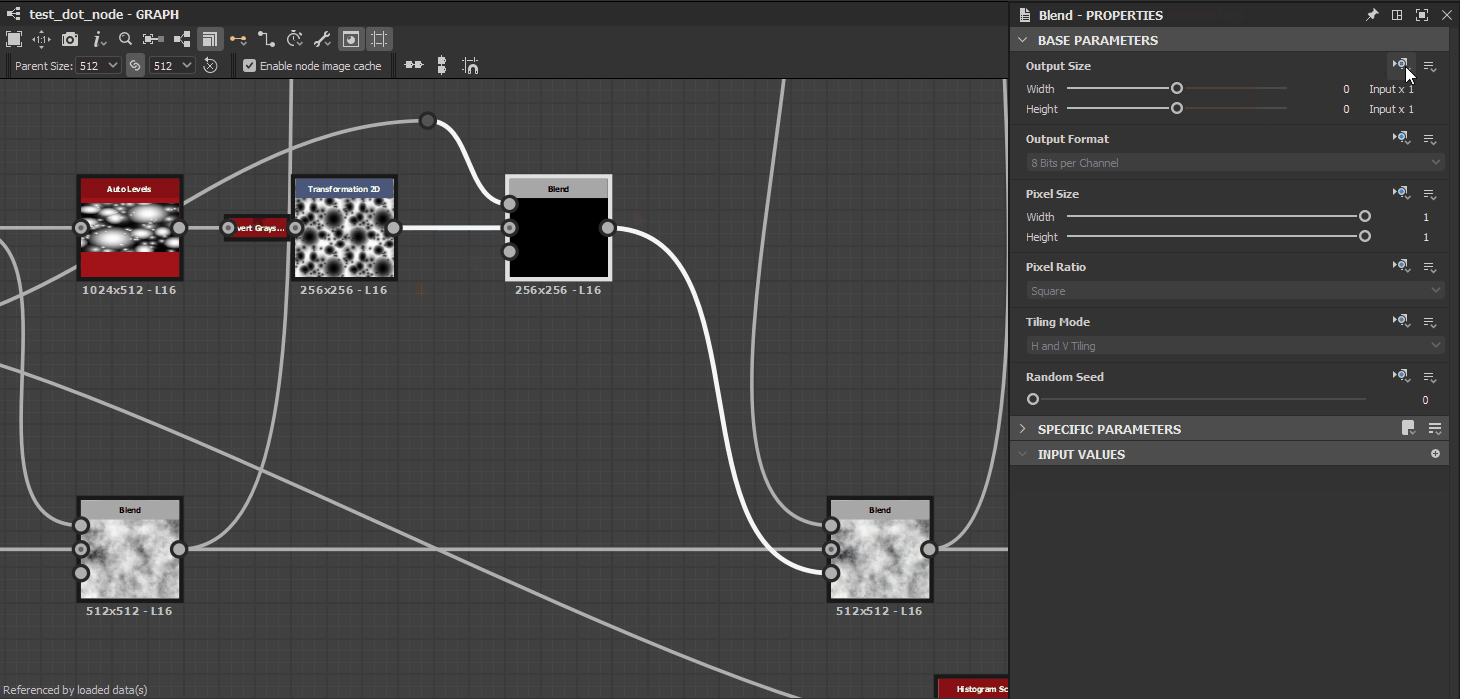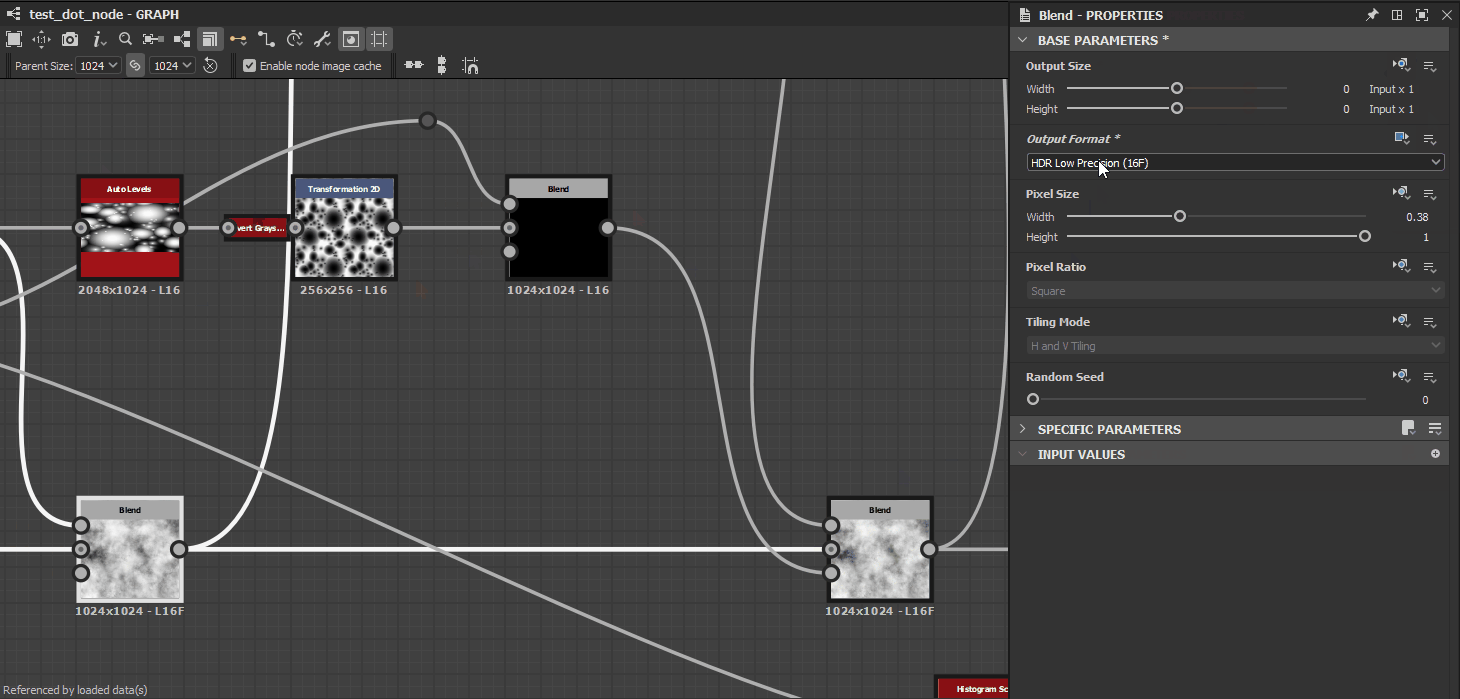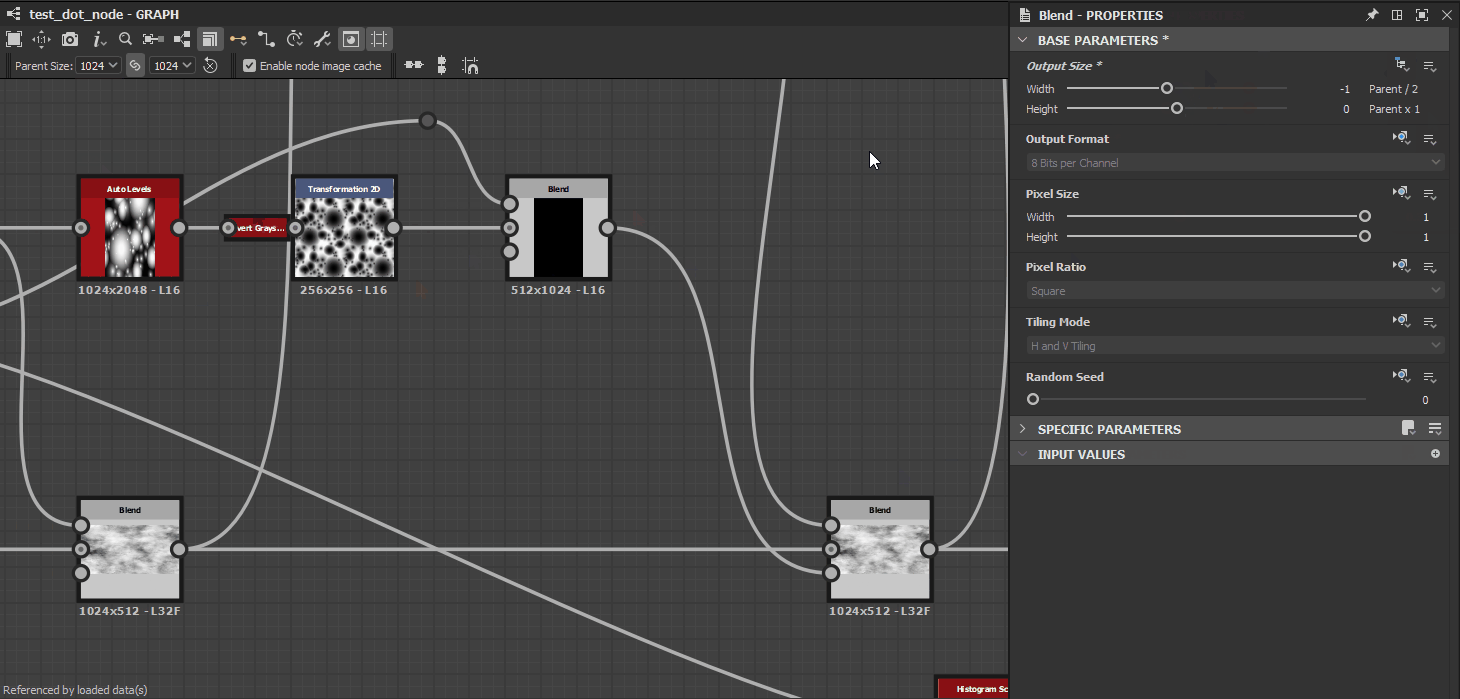

Inheritance methods are applied for a node’s Base parameters, which is the set of common parameters all nodes have which control fundamental aspects of their behaviour. These parameters include:
- Output Size
- Output Format (i.e., bitdepth)
- Pixel Size
- Pixel Ratio
- Tiling Mode
- Random Seed
This should let you appreciate how changes in one node may impact the resolution, precision, and tiling behaviour of all nodes downstream from it.
An important reminder for understanding the concepts discussed in this page: an instance node is a node representing a graph in another graph, with its own discrete parameter values, hence the term instance.
E.g., two Perlin noise nodes in a same graph are both representations of a same source graph (perlin_noise in noise_perlin_noise.sbs) with their own sets of parameter values.
Output size: Use the ![]() lock button to have the Height value match the Width value
lock button to have the Height value match the Width value
Random seed: Use the ![]() button to assign a new random value to the random seed.
button to assign a new random value to the random seed.
Changing inheritance methods
In the Properties panel, all parameters listed in the Base parameters section of a node’s properties have a (icon) Set inheritance method dropdown button opposite to their label.
This button lets you select the inheritance method which should be used to for a parameter.
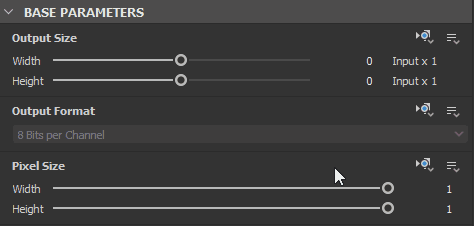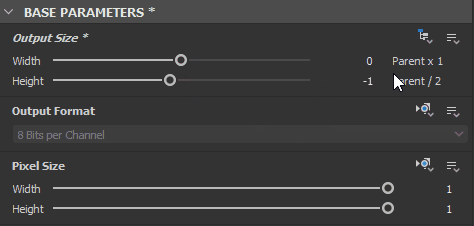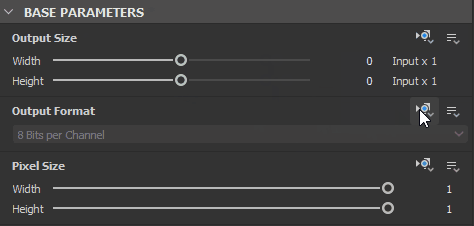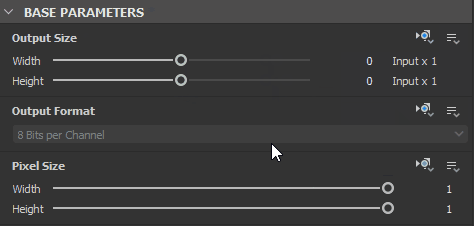

In most cases, a node’s Base parameters are set to Relative to input, to leverage the procedural behaviour of chaining nodes together, while a graph’s Base parameters are set to Relative to parent, so the global parameters can adapt to the context the graph is used in.
TWEAKING INHERITED VALUES
Some Base parameters, such as Output Size, Pixel Size or Random Seed, can be changed relatively to the inherited value.
For instance, when the Output Size parameter uses a Relative to... inheritance method, a value or (1, -1) means one power of two resolution above the inherited value for X and one power of two resolution below the inherited value for Y such as:
- Inherited value :
(9, 9)which is2^9, 2^9 = 512, 512 - Relative value:
(1, -1)which is2^(9+1), 2^(9-1) = 256, 1024
The Output Size page digs deeper into this critical Base parameter, and is recommeded reading to understand how the final resolution of a node is computed.
If a function is applied to a Base parameter, the result of the function will also be interpreted using the parameter's inheritance method.
Keeping the Output Size example in mind, a function aiming at increasing the inherited resolution twofold in X and Y should output the (2, 2) Integer2 value.
Parenthood for nodes and graphs
When using the Relative to parent inheritance method, you should understand what exactly that parent is in a specific context.
The parent of a node is the graph it exists in.
The parent of a graph is the context it exists in:
- If that graph is a sub-graph instantiated into another host graph as an instance node, then the parent of the sub-graph is the instance node. The parent of that instance node is the host graph.
- If that graph is a root graph, then the parent is the application itself and whatever value the application has set for a given parameter. For instance, graphs will inherit from the Parent Size parameter set in the Graph view’s toolbar.
Parenthood is applied as-is when publishing a package to Substance 3D asset files (SBSAR). This means setting any parameter to the Absolute inheritance method will lock that parameter to its current value in the published asset.
While this is desirable for Bitmap nodes or optimisation purposes, for instance, we strongly recommend using Relative to… inheritance methods when working in Substance graphs unless there is a clear, deliberate purpose in doing otherwise.
IN-CONTEXT EDITING
When using In-context editing on a graph instance node, the parent of the graph is the instance node. In that case, the Parent Size setting in the Graph view’s toolbar is disabled, as the graph inherits is base parameters from the instance node.
This trait is the point of in-context editing and should be factored in when setting inheritance method and assessing the current values of any node’s Base parameters.


Relative to input
The input inherits from its discrete input data, regardless of the graph’s Base parameters. This is very helpful for controlling data per input.


Relative to parent
The input inherits from the graph, and the data it receives is adapted accordingly.
Primary input






One of the inputs may be set as the graph’s Primary input, by clicking RMB on that Input node and selecting the Set as Primary Input option in the contextual menu.


When the graph is instanced into another graph as an instance node, all the instance node’s Base parameters which are set to Relative to input will inherit the data connected to that input. The Primary input of an instance node may be identified by the small dark dot in its connector.
The other inputs which are set to Relative to parent will inherit the same Base parameters’ values, as they inherit from the graph which inherits from the instance node*, which inherits from the Primary input.
*: This is true is the graph uses the Relative to parent inheritance method.
Examples
Here are some examples covering different cases of inheritance, and the interplay of the inheritance methods set in the following actors, from top to bottom:
- Application
- Host graph
- Instance node in host graph
- Sub-graph – i.e., the graph referenced by the instance node
- Nodes in sub-graph
The inheritance method set for an actor is displayed in orange just above it. The flow of inheritance to its source is displayed with orange lines.
Letters represent separate sets of Base parameters, and should help follow what data is inherited by which actor.
Example A


Example B


Example C


Example D


Troubleshooting inheritance issues
As you build your graph and increase its complexity, you may run into unexpected results caused by inheritance. If the output of a node has an incorrect resolution or precision (i.e., bitdepth), you should go up the inheritance chain to pinpoint where these values come from.
A good starting point is checking the data displayed just below a node: these are the resolution, color format and precision of the image output by the first output of the node. While understanding the resolution is straightforward, the second piece of data is worth detailing:
- The letter prefix refer to the image’s color format:
- L: Luminance (i.e., grayscale)
- C: Color
- The number refer to the image’s bitdepth, from lowest to highest precision:
- 8: 8-bit integer (256 steps in 0-1)
- 16: 16-bit integer (65 536 steps in 0-1)
- 16F: 16-bit floating point (low precision values beyond 0-1, including negatives)
- 32F: 32-bit floating point (high precision values beyond 0-1, including negatives)
If the node has more than one output, you can check their resolution and precision in two easy ways:
- Double-click LMB on the output connector to display the image in the 2D view, and check the image information displayed on the bottom left corner of the 2D view’s viewport
- Create a Levels or Transformation 2D node and connect its input to the output you want to check. The node will inherit from the output by default, and you can then check the values below the node.
Now you can go up the node chain in the graph and try to find the first node where the unexpected values appear. Check the inheritance method of its Base parameters.
If nothing is amiss and the node is an instance node, you need to go deeper and open the graph referenced by that instance node. Repeat the process starting from the graph’s Output nodes and going upstream.
A COMMON EXAMPLE
In particular, the Primary input concept is easily overlooked and can result in inheritance issues.
The Blend node is very susceptible to this, as it is used very frequently. Its Background input is its Primary input.


You need to pay attention to the order in which you blend the two inputs: the input which resolution and precision you wish to retain down the graph should be connected to the Background input, if the blending mode you need makes it possible. If not, then you may need to tweak the Blend node’s Base parameters and their inheritance method to compensate.