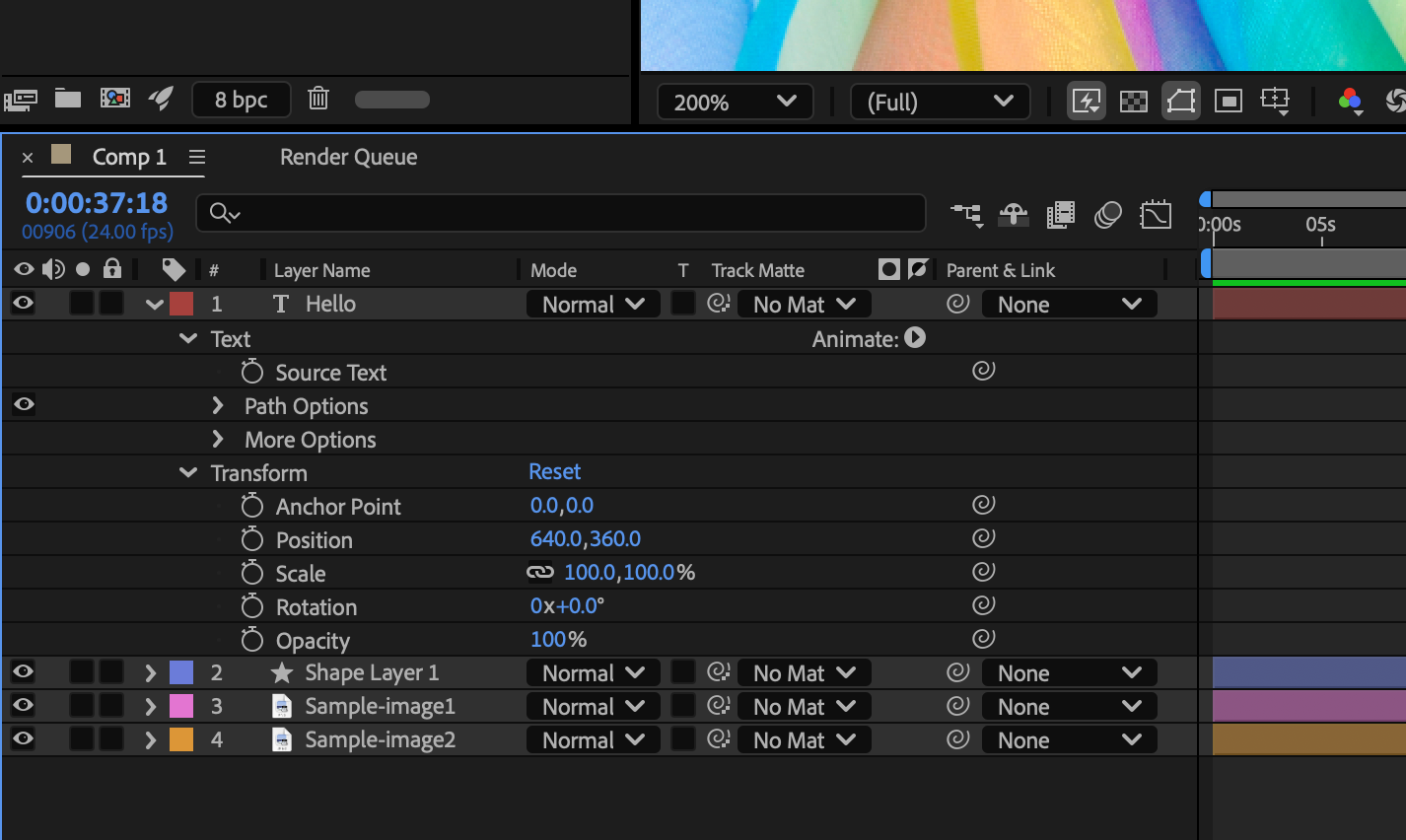
In the Timeline panel, show the layer property containing the value you want to copy.
- After Effects User Guide
- Beta releases
- Getting started
- Workspaces
- Projects and compositions
- Importing footage
- Preparing and importing still images
- Importing from After Effects and Adobe Premiere Pro
- Importing and interpreting video and audio
- Preparing and importing 3D image files
- Importing and interpreting footage items
- Import SVG files
- Working with footage items
- Detect edit points using Scene Edit Detection
- XMP metadata
- Text and Graphics
- Text
- Motion Graphics
- Work with Motion Graphics templates in After Effects
- Use expressions to create drop-down lists in Motion Graphics templates
- Work with Essential Properties to create Motion Graphics templates
- Replace images and videos in Motion Graphics templates and Essential Properties
- Animate faster and easier using the Properties panel
- Variable Font Axes
- Drawing, Painting, and Paths
- Overview of shape layers, paths, and vector graphics
- Paint tools: Brush, Clone Stamp, and Eraser
- Taper shape strokes
- Shape attributes, paint operations, and path operations for shape layers
- Use Offset Paths shape effect to alter shapes
- Creating shapes
- Create masks
- Remove objects from your videos with the Content-Aware Fill panel
- Roto Brush and Refine Matte
- AI-powered Object Matte
- Create Nulls for Positional Properties and Paths
- Layers, Markers, and Camera
- Animation, Keyframes, Motion Tracking, and Keying
- Animation
- Keyframe
- Motion tracking
- Keying
- Transparency and Compositing
- Adjusting color
- Effects and Animation Presets
- Effects and animation presets overview
- Effect list
- Effect Manager
- Simulation effects
- Stylize effects
- Audio effects
- Distort effects
- Perspective effects
- Channel effects
- Generate effects
- Time effects
- Transition effects
- The Rolling Shutter Repair effect
- Blur and Sharpen effects
- 3D Channel effects
- Utility effects
- Matte effects
- Noise and Grain effects
- Detail-preserving Upscale effect
- Obsolete effects
- Cycore plugins
- Expressions and Automation
- Expressions
- Expression basics
- Understanding the expression language
- Using expression controls
- Syntax differences between the JavaScript and Legacy ExtendScript expression engines
- Editing expressions
- Expression errors
- Using the Expressions editor
- Use expressions to edit and access text properties
- Expression language reference
- Expression examples
- Automation
- Expressions
- Immersive video, VR, and 3D
- Construct VR environments in After Effects
- Apply immersive video effects
- Compositing tools for VR/360 videos
- Advanced 3D Renderer
- Import and add 3D models to your composition
- Import 3D models from Creative Cloud Libraries
- Create parametric meshes
- Image-Based Lighting
- Animated Environment Lights
- Enable lights to cast shadows
- Extract and animate lights and cameras from 3D models
- Tracking 3D camera movement
- Adjust Default Camera Settings for 3D compositions
- Cast and accept shadows
- Embedded 3D model animations
- Shadow Catcher
- 3D depth data extraction
- Enable in‑engine Depth of Field in Advanced 3D
- Modify materials properties of a 3D layer
- Apply Substance 3D materials
- Work in 3D Design Space
- 3D Transform Gizmos
- Single 3D Gizmo for multiple 3D layers
- Do more with 3D animation
- Preview changes to 3D designs real time with the Mercury 3D engine
- Stereoscopic 3D in After Effects
- Add responsive design to your graphics
- Views and Previews
- Rendering and Exporting
- Basics of rendering and exporting
- H.264 Encoding in After Effects
- Export an After Effects project as an Adobe Premiere Pro project
- Converting movies
- Multi-frame rendering
- Automated rendering and network rendering
- Rendering and exporting still images and still-image sequences
- Using the GoPro CineForm codec in After Effects
- Working with other applications
- Collaboration: Frame.io, and Team Projects
- Memory, storage, performance
- Knowledge Base
Learn how to work with layer properties and adjust them to animate various attributes of layers, including transform properties, effects, masks, and layer styles.
Each layer has properties, many of which you can modify and animate. The basic group of properties that every layer has is the Transform group, which includes Position and Opacity properties. When you add certain features to a layer, for example, by adding masks or effects or by converting the layer to a 3D layer—the layer gains additional properties collected in property groups.
All layer properties are temporal—they can change the layer over time. Some layer properties, such as Opacity, have only a temporal component. Some layer properties, such as Position, are also spatial—they can move the layer or its pixels across composition space.
You can expand the layer outline to display layer properties and change property values.
Most properties have a stopwatch . Any property with a stopwatch can be animated. Learn more about animation, keyframes, and expressions.
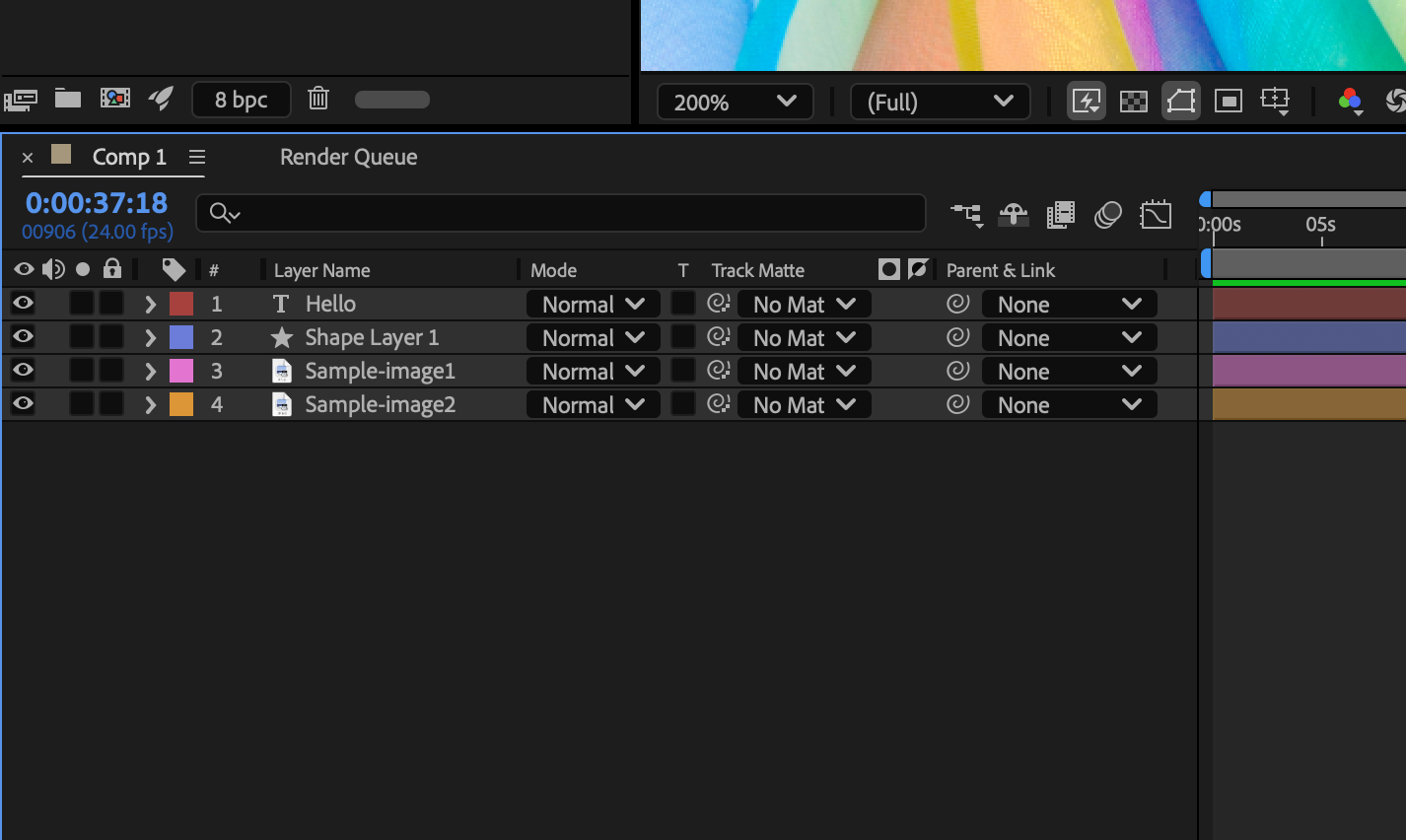
An example of collapsed and expanded property group of a layer in the Timeline panel.
Properties in the Effects property group (effect properties) are also layer properties. Many effect properties can also be modified in the Effect Controls panel.
- To expand or collapse a property group, select the triangle to the left of the layer name or property group name.
- To expand or collapse a property group and all of its children, Ctrl-click (Windows) or Command-click (macOS) the triangle.
- To expand or collapse all groups for selected layers, use Ctrl+` (accent grave) (Windows) or Command+` (accent grave) (macOS).
- To reveal an effect property in the Timeline panel, double-click the property name in the Effect Controls panel.
- To hide a property or property group, Alt+Shift-click (Windows) or Option+Shift-click (macOS) the name in the Timeline panel.
- To show only the selected properties or property groups in the Timeline panel, press SS.
The SS shortcut is especially useful for working with paint strokes. Select the paint stroke in the Layer panel, and press SS to open the property group for that stroke in the Timeline panel.
- To show only a specific property or property group, press its shortcut key or keys. Learn more about using keyboard shortcuts to show properties and groups in the Timeline panel.
- To add a property or property group to the properties shown in the Timeline panel, hold Shift while pressing the shortcut key for the property or property group.
- To show only properties modified from their default values, press UU or select Animation > Reveal Modified Properties.
- To show only properties with keyframes or expressions, press U or select Animation > Reveal Animating Properties.
The U and UU commands are handy for learning how animation presets, template projects, or other animated items work because they isolate the properties that you modified.
You can also filter layers in the Timeline panel to show only those with properties matching a search string. Learn more about searching and filtering in the Timeline, Project, and Effects & Presets panels.


- To select a property or property group—including all values, keyframes, and expressions—select the name in the layer outline in the Timeline panel.
- To copy properties from one layer or property group to another, select the layer, property, or property group, use Ctrl + C (Windows) or Command + C (macOS), select the target layer, property, or property group, and use Ctrl + V (Windows) or Command + V (macOS).
- To duplicate a property group, select it and press Ctrl + D (Windows) or Command + D (macOS).
You can only duplicate some property groups, including shapes, masks, and effects. However, you can’t duplicate top-level property groups such as Contents, Masks, Effects, and Transforms. If you attempt to duplicate a top-level property group, the entire layer is duplicated instead.
You can copy the current value of a layer property to another layer, even when the original layer contains no keyframes.
-
-
Select the name of the layer property to select it.
-
Select Edit > Copy.
-
Select the layer into which you want to paste the value.
-
If the target layer contains keyframes, move the current-time indicator to the time where you want to paste the value. If the target layer does not contain keyframes, the new value applies to the entire duration of the layer.
-
Select Edit > Paste.
If multiple layers are selected and you change a property for one layer, then the property is changed for all selected layers. Sliders, angle controls, and some other property controls are only available in the Effect Controls panel.
To change the units for a property, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (macOS) the underlined value, select Edit Value, and choose from the Units menu. The available units are different for different property types. You can’t change the units for some properties.
- Place the pointer over the underlined value and drag it to the left or right.
- Select the underlined value, enter a new value, and then use Enter (Windows) or Return (macOS).
You can enter simple arithmetic expressions for property values and other number entries. For example, you can enter 2*3 instead of 6, 4/2 instead of 2, and 2e2 instead of 200. Such entries can be especially useful when incrementing a value by a specific amount from its original value.
- Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (macOS) the underlined value and select Edit Value.
- Drag the slider left or right.
- Select a point inside the angle control or drag the angle control line.
After you click inside the angle control, you can drag outside it for more precision.
- To increase or decrease the property value by 1 unit, click the underlined value and press the Up Arrow or Down Arrow key. To increase or decrease by 10 units, hold Shift while pressing the Up Arrow or Down Arrow key. To increase or decrease by 0.1 units, hold Ctrl (Windows) or Command (macOS) while pressing the Up Arrow or Down Arrow key.
- To reset properties in a property group to their default values, select Reset next to the property group name. To reset an individual property, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (macOS) the property name (not the value) and select Reset from the context menu.
If the property contains keyframes, a keyframe is added at the current time with the default value.
Transformations, such as rotation and scale, occur around the anchor point (sometimes called transformation point or transformation center) of the layer. By default, the anchor point ![]() for most layer types is at the center of the layer.
for most layer types is at the center of the layer.
Though there are times when you’ll want to animate the anchor point, it’s most common to set the anchor point for a layer before you begin animating. For example, if you’re animating an image of a person made up of one layer for each body part, you’ll probably want to move the anchor point of each hand to the wrist area so that the hand rotates around that point for the whole animation.
The easiest way to pan and scan over a large image is to animate Anchor Point and Scale properties.
- Drag the anchor point using the Selection tool in the Layer panel
Layers of some types, such as text layers and shape layers, can’t be opened in the Layer panel.
- To move a layer anchor point 1 pixel, select Anchor Point Path from the View menu at the lower-right area of the Layer panel, and press an arrow key. To move 10 pixels, hold Shift as you press an arrow key. Pixel measurements are at the current magnification in the Layer panel.
- To move a layer anchor point in the Composition panel without moving the layer, select the layer and use the Pan Behind (Anchor Point) tool
 to drag the anchor point.
to drag the anchor point.
Moving an anchor point with the Pan Behind (Anchor Point) tool changes Position and Anchor Point values so that the layer remains where it was in the composition before you moved the anchor point. To change only the Anchor Point value, Alt-drag (Windows) or Option-drag (macOS) with the Pan Behind (Anchor Point) tool.
Reset a layer anchor point
- To reset the anchor point to its default location in the layer, double-click the Pan Behind (Anchor Point) tool
 button in the Tools panel.
button in the Tools panel. - To reset the anchor point to its default location in the layer, Alt-double-click (Windows) or Option-double-click (macOS) the Pan Behind (Anchor Point) tool button. The layer moves to the center of the composition.
Set layer anchor point to center of content
You can set the anchor point to be in the center of the layer content in any of the following ways:
- Select Layer > Transform > Center Anchor Point In Layer Content
- Use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + Home (Windows) or Command + Option + Home (macOS)
- Ctrl + double-click (Windows) or Command + double-click (macOS) the Pan Behind (Anchor Point) tool
Here are a few uses of this command:
- Setting the anchor point of a shape layer to the center of a single shape or to the centroid of a group of shapes in a shape layer.
- Setting the anchor point for a text layer to the center of the text content.
- Setting the anchor point of a layer to the center of the visible area within a masked region.
Use new beta features
Quick Set Anchor is now available for testing and feedback. Try it now in After Effects (beta).
In the latest After Effects (beta), you can use Quick Set Anchor, a more efficient way to change the anchor point on your 2D layers to any of nine commonly used points — all the corners and centers of your layer’s edges. You can access Quick Set Anchor from the Properties panel or the keyboard shortcut – Shift + Tab.
Quick Set Anchor can be launched by selecting a layer and then selecting the Anchor Point icon next to the Anchor Point property in the Properties panel. This opens a temporary pop-over Quick Set Anchor dialog. You can then drag your cursor to the anchor point while pressing the mouse button or select it from the pop-over.


You can also launch the Quick Set Anchor dialog exactly where your cursor is placed by using the keyboard shortcut Shift+Tab. Selecting any point in the Quick Set Anchor dialog will update the anchor point for all selected layers and close the dialog. To close the dialog without making changes, click anywhere outside it.


Join the conversation about Quick Set Anchor in the After Effects (Beta) community.
As with other transformations, the scaling of a layer occurs around the anchor point of the layer. If you move the anchor point away from the center of the layer, the layer may move when you flip it. Some layers—such as camera, light, and audio-only layers—don’t have a Scale property.
To flip a layer is to multiply the horizontal or vertical component of its Scale property value by -1. A layer flips around its anchor point.
You can scale a layer beyond the composition frame. Learn about scaling exponentially, as with a zoom lens and scaling or resizing entire movies rather than a single layer.
- To flip selected layers, select Layer > Transform > Flip Horizontal or Layer > Transform > Flip Vertical.
- To scale a layer proportionally in the Composition panel, Shift-drag any layer handle.
- To scale a layer freely in the Composition panel, drag a corner layer handle.
- To scale one dimension only in the Composition panel, drag a side layer handle.
- To increase or decrease Scale for a selected layer by 1%, hold down Alt (Windows) or Option (macOS) as you press + or – on the numeric keypad.
- To increase or decrease Scale for selected layers by 10%, hold down Alt+Shift (Windows) or Option+Shift (macOS) as you press + or – on the numeric keypad.
- To scale an entire composition, select File > Scripts > Scale Composition.jsx.
- To scale and center selected layers to fit in the composition frame, select Layer > Transform > Fit To Comp.
- To scale and center selected layers to fit the width or height of the composition frame, while preserving the aspect ratio of the layer, select Layer > Transform > Fit To Comp Width or Fit To Comp Height.
- To scale a layer proportionally in the Timeline panel, select the layer, press S to display the Scale property, select the Constrain Proportions icon to the left of the Scale values, and enter a new value for the x, y, or z scale.
To activate the Constrain Proportions icon and match the height to the width, Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (macOS) it.
- To scale to a specific set of pixel dimensions, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (macOS) the Scale value in the Timeline panel, select Edit Value, and change the units to pixels in the Scale dialog box. Select Include Pixel Aspect Ratio to see and adjust dimensions in terms of the composition’s pixel aspect ratio.
Scaling down a raster (non-vector) layer sometimes causes a slight softening or blurring of the image. Scaling up a raster layer by a large factor can cause the image to appear blocky or pixelated.
The Detail-preserving Upscale effect is capable of scaling up images by large amounts while preserving details in the image.
You can choose between bicubic and bilinear sampling for selected layers, which determines how pixels are sampled for scaling and for all transformations applied using the Transform effect. Learn more about working with layer image quality and subpixel positioning.
Adobe Photoshop provides fine control over resampling methods used for scaling of images. For fine control of resampling, you can export frames to Photoshop to change the image size and then import the frames back into After Effects.
Though it's not very well suited for movies, the content-aware scaling feature in Photoshop is very useful for extending and scaling still images. This feature can be useful when repurposing images for wide-screen formats that were created for standard-definition formats.
As with other transformations, rotation of a layer occurs around the anchor point of the layer.
To reveal the Rotation property value for selected layers in the Timeline panel, use the keyboard shortcut - R.
The first part of the Rotation property value is the number of whole rotations; the second part is the fractional rotation in degrees.
- To rotate a layer by dragging in the Composition panel, drag the layer using the Rotation tool. To constrain the rotation to 15° increments, hold down Shift as you drag.
- To rotate selected layers by 1 degree, press + (Plus) or - (Minus) on the numeric keypad.
- To rotate selected layers by 10 degrees, press Shift + + (Plus) or Shift + - (Minus) on the numeric keypad.
You can turn a 3D layer by changing its Orientation or Rotation values. Learn about how to rotate or orient a 3D layer.
When you use footage containing audio, the default audio level for playback is 0 dB, meaning that the level is unadjusted in After Effects. Setting a positive decibel level increases volume, and setting a negative decibel level decreases volume.
Double-clicking an Audio Levels keyframe activates the Audio panel.
The VU meter in the Audio panel displays the volume range for the audio as it plays. The red blocks at the top of the meter represent the volume limit of your system.
For more precision in setting audio levels by dragging sliders, increase the height of the Audio panel.
To adjust volume, do one of the following in the Audio panel:
To set the level of the left and right channels together, drag the center slider up or down.
To set the level of the left channel, drag the left slider up or down, or type a new value in the levels box at the bottom of the left slider.
To set the level of the right channel, drag the right slider up or down, or type a new value in the levels box at the bottom of the right slider.
To synchronize changes to layers by assigning one layer’s transformations to another layer, use parenting. After a layer is made a parent to another layer, the other layer is called the child layer. When you assign a parent, the transform properties of the child layer become relative to the parent layer instead of to the composition. For example, if a parent layer moves 5 pixels to the right of its starting position, then the child layer also moves 5 pixels to the right of its position. Parenting is similar to grouping; transformations made to the group are relative to the anchor point of the parent.
Parenting affects all transform properties such as Position, Scale, Rotation, and Orientation (for 3D layers), but not Opacity.
When parenting layers, helpful text describing alternate parenting behaviors is displayed on the layer bar below the cursor position and in the Info panel.
A layer can have only one parent, but a layer can be a parent to any number of layers in the same composition.
You can animate child layers independent of their parent layers. You can also parent using null objects, which are hidden layers.
You cannot animate the act of assigning and removing the parent designation—that is, you cannot designate a layer as a parent at one point in time and designate it as a normal layer at a different point in time.
When you create a parenting relationship, you can choose whether to have the child take on the transform property values of the parent or retain its own. If you choose to have the child take on the transform property values of the parent, the child layer jumps to the parent’s position. If you choose to have the child retain its own transform property values, then the child stays where it is. In both cases, subsequent changes to the transform property values of the parent are applied to the child. Similarly, you can choose whether the child jumps when the parenting relationship is removed.
When parenting layers, you can use the Shift key to move the child layer to the location of the parent. This can be useful when you want to attach a layer to a null, but have the layer move to the location of the parent null (for example, attaching a 3D text layer to a null layer created from the 3D Camera Tracker).


- To show or hide the Parent column in the Timeline panel, select Columns > Parent from the Timeline panel menu.
- To parent a layer, in the Parent column, drag the pick whip from the layer that is to be the child layer to the layer that is to be the parent layer.
- To parent a layer, in the Parent column, select the menu of the layer that you want to be the child, and select a parent layer name from the menu.
- To remove a parent from a layer, in the Parent column, select the menu of the layer to remove the parent from, and select None.
- To extend the selection to include all child layers of a selected parent layer, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (macOS) the layer in the Composition or Timeline panel, and select Select Children.
- To make a child layer jump when a parent is assigned or removed, hold down Alt (Windows) or Option (macOS) as you assign or remove the parent.
- To remove a parent from a layer (that is, set Parent to None), Ctrl-click (Windows) or Command-click (macOS) the parenting pick whip of the child layer in the Timeline panel. Alt+Ctrl-click (Windows) or Option+Command-click (macOS) the parenting pick whip of the child layer to remove the parent and cause the child layer to jump.
To assign a parent layer, but keep that layer from being a visible element in your project, use a null object. A null object is an invisible layer that has all the properties of a visible layer so that it can be a parent to any layer in the composition. Adjust and animate a null object as you would any other layer. You use the same commands to modify settings for a null object that you use for a solid-color layer (Layer > Solid Settings).
You can apply Expression Controls effects to null objects and then use the null object as a control layer for effects and animations in other layers. For example, when working with a camera or light layer, create a null object layer and use an expression to link the Point Of Interest property of the camera or light to the Position property of the null layer. Then, you can animate the Point Of Interest property by moving the null object. It is often easier to select and see a null object than it is to select and see the point of interest.
A composition can contain any number of null objects. A null object is visible only in the Composition and Layer panels and appears in the Composition panel as a rectangular outline with layer handles. Effects are not visible on null objects.
To create a null object, select the Timeline or Composition panel and select Layer > New > Null Object.
- The anchor point of a new null object layer appears in the upper-left corner of the layer, and the layer is anchored in the center of the composition at its anchor point. Change the anchor point as you would for any other layer.
- If a null object is visually distracting in your composition frame, consider dragging it out of the frame, onto the pasteboard.
You can also use Nulls Controllers for Positional Properties to create Nulls to control the positional properties and movement of objects makes your work in After Effects easier, especially when you have many layers or complicated animations. It lets you isolate and control the movement of a specific point (such as a Position or an Anchor Point within a Shape, object, or layer) independently from other elements of the same layer.
You can create guide layers from existing layers to use for reference in the Composition panel, to help you position and edit elements. For example, you can use guide layers for visual reference, for audio timing, for timecode reference, or for storing comments to yourself.
A guide layer icon appears next to the name of a guide layer or its source in the Timeline panel.
By default, guide layers aren’t rendered when you create an output but can be rendered when desired by changing the render settings for the composition.
Guide layers in nested compositions can’t be viewed in the containing composition.
- To convert selected layers to guide layers, select Layer > Guide Layer.
- To render a composition with its visible guide layers, select Render Settings in the Render Queue panel, and then select Current Settings from the Guide Layers menu in the Render Settings dialog box.
- To render a composition without rendering guide layers, select Render Settings in the Render Queue panel, and choose All Off from the Guide Layers menu in the Render Settings dialog box.