Select the 3D Layer switch for the layer in the Timeline panel, or select the layer and select Layer > 3D Layer.
- After Effects User Guide
- Beta releases
- Getting started
- Workspaces
- Projects and compositions
- Importing footage
- Preparing and importing still images
- Importing from After Effects and Adobe Premiere Pro
- Importing and interpreting video and audio
- Preparing and importing 3D image files
- Importing and interpreting footage items
- Import SVG files
- Working with footage items
- Detect edit points using Scene Edit Detection
- XMP metadata
- Text and Graphics
- Text
- Motion Graphics
- Work with Motion Graphics templates in After Effects
- Use expressions to create drop-down lists in Motion Graphics templates
- Work with Essential Properties to create Motion Graphics templates
- Replace images and videos in Motion Graphics templates and Essential Properties
- Animate faster and easier using the Properties panel
- Variable Font Axes
- Drawing, Painting, and Paths
- Overview of shape layers, paths, and vector graphics
- Paint tools: Brush, Clone Stamp, and Eraser
- Taper shape strokes
- Shape attributes, paint operations, and path operations for shape layers
- Use Offset Paths shape effect to alter shapes
- Creating shapes
- Create masks
- Remove objects from your videos with the Content-Aware Fill panel
- Roto Brush and Refine Matte
- AI-powered Object Matte
- Create Nulls for Positional Properties and Paths
- Layers, Markers, and Camera
- Animation, Keyframes, Motion Tracking, and Keying
- Animation
- Keyframe
- Motion tracking
- Keying
- Transparency and Compositing
- Adjusting color
- Effects and Animation Presets
- Effects and animation presets overview
- Effect list
- Effect Manager
- Simulation effects
- Stylize effects
- Audio effects
- Distort effects
- Perspective effects
- Channel effects
- Generate effects
- Time effects
- Transition effects
- The Rolling Shutter Repair effect
- Blur and Sharpen effects
- 3D Channel effects
- Utility effects
- Matte effects
- Noise and Grain effects
- Detail-preserving Upscale effect
- Obsolete effects
- Cycore plugins
- Expressions and Automation
- Expressions
- Expression basics
- Understanding the expression language
- Using expression controls
- Syntax differences between the JavaScript and Legacy ExtendScript expression engines
- Editing expressions
- Expression errors
- Using the Expressions editor
- Use expressions to edit and access text properties
- Expression language reference
- Expression examples
- Automation
- Expressions
- Immersive video, VR, and 3D
- Construct VR environments in After Effects
- Apply immersive video effects
- Compositing tools for VR/360 videos
- Advanced 3D Renderer
- Import and add 3D models to your composition
- Import 3D models from Creative Cloud Libraries
- Create parametric meshes
- Image-Based Lighting
- Animated Environment Lights
- Enable lights to cast shadows
- Extract and animate lights and cameras from 3D models
- Tracking 3D camera movement
- Adjust Default Camera Settings for 3D compositions
- Cast and accept shadows
- Embedded 3D model animations
- Shadow Catcher
- 3D depth data extraction
- Enable in‑engine Depth of Field in Advanced 3D
- Modify materials properties of a 3D layer
- Apply Substance 3D materials
- Work in 3D Design Space
- 3D Transform Gizmos
- Single 3D Gizmo for multiple 3D layers
- Do more with 3D animation
- Preview changes to 3D designs real time with the Mercury 3D engine
- Stereoscopic 3D in After Effects
- Add responsive design to your graphics
- Views and Previews
- Rendering and Exporting
- Basics of rendering and exporting
- H.264 Encoding in After Effects
- Export an After Effects project as an Adobe Premiere Pro project
- Converting movies
- Multi-frame rendering
- Automated rendering and network rendering
- Rendering and exporting still images and still-image sequences
- Using the GoPro CineForm codec in After Effects
- Working with other applications
- Collaboration: Frame.io, and Team Projects
- Memory, storage, performance
- Knowledge Base
3D layers overview and resources
When you make a layer a 3D layer, the layer itself remains flat, but it gains additional properties - Position (z), Anchor Point (z), Scale (z), Orientation, X Rotation, Y Rotation, Z Rotation, Geometry Options, and Material Options.
- Material Options properties specify how the layer interacts with light and shadows. Only 3D layers interact with shadows, lights, and cameras.
- Geometry Options properties allow you to apply a beveled edge to a shape or text to add depth to the object and give it a more three-dimensional look.

An example of a 2D layer transformed into a 3D layer with additional 3D properties modified.
Individual characters within text layers can optionally be 3D sublayers, each with their own 3D properties. A text layer with Enable Per-character 3D selected (Animate > Enable Per-character 3D) behaves just like a precomposition that consists of a 3D layer for each character. All camera and light layers have 3D properties.
By default, layers are at a depth (z-axis position) of 0. In After Effects, the origin of the coordinate system is at the upper-left corner; x (width) increases from left to right, y (height) increases from top to bottom, and z (depth) increases from near to far. Some video and 3D applications use a coordinate system that is rotated 180 degrees around the x axis ; in these systems, y increases from bottom to top, and z increases from far to near.
You can transform a 3D layer relative to the coordinate space of the composition, the coordinate space of the layer, or a custom space by selecting an axis mode.
You can add effects and masks to 3D layers, composite 3D layers with 2D layers, and create and animate camera and light layers to view or illuminate 3D layers from any angle. When rendering for final output, 3D layers are rendered from the perspective of the active camera.
All effects are 2D, including effects that simulate 3D distortions. For example, viewing a layer with the Bulge effect from the side does not show a protrusion.
As with all masks, mask coordinates on a 3D layer are in the 2D coordinate space of the layer.
Convert 3D layers
When you convert a layer to 3D, a depth (z) value is added to its Position, Anchor Point, and Scale properties, and the layer gains Orientation, Y Rotation, X Rotation, Geometry Options, and Material Options properties. The single Rotation property is renamed Z Rotation. When you convert a 3D layer back to 2D, these properties are removed, including all values, keyframes, and expressions, and the values cannot be restored by converting the layer back to a 3D layer. The Anchor Point, Position, and Scale properties remain, along with their keyframes and expressions, but their z values are hidden and ignored.
Convert a layer to a 3D layer
-
Use the 3D Layer switch for a layer to transform it into a 3D object, enabling it to be adjusted in three-dimensional space. Use the 3D Layer switch for a layer to transform it into a 3D object, enabling it to be adjusted in three-dimensional space.
Convert a text layer to a 3D layer with per-character 3D properties enabled
-
Select Animation > Animate Text > Enable Per-Character 3D, or select Enable Per-Character 3D from the Animate menu for the layer in the Timeline panel.
Use the Enable Per-character 3D to transform each character in a text layer into separate 3D objects. Use the Enable Per-character 3D to transform each character in a text layer into separate 3D objects.
Convert a 3D layer to a 2D layer
-
Deselect the 3D Layer switch for the layer in the Timeline panel, or select the layer and the Layer > 3D Layer.
Show or hide 3D axes and layer controls
3D axes are color-coded arrows: red for x, green for y, and blue for z.
- To show or hide 3D axes, camera and light wireframe icons, layer handles, and the point of interest, select View > Show Layer Controls.


If the axis that you want to manipulate is difficult to see, try a different setting in the Select view layout menu at the lower-right corner of the Composition panel.
- To show or hide a set of persistent 3D reference axes, select the Grid And Guides Options button at the bottom of the Composition panel, and select 3D Reference Axes.


Move a 3D layer
-
Select the 3D layer that you want to move.
-
Do one of the following:
- In the Composition panel, use the Selection tool to drag the arrowhead of the 3D axis layer control corresponding to the axis along which you want to move the layer. Shift-drag to move the layer more quickly.
- In the Timeline panel, modify the Position property values.
TipUse P on the keyboard to show the Position property of the layer.
- To move selected layers so that their anchor points are at the center in the current view, select Layer > Transform > Center In View or use Ctrl+Up Arrow (Windows) or Command+Up Arrow (macOS).
Rotate or orient a 3D layer
You can turn a 3D layer by changing its Orientation or Rotation values. In both cases, the layer turns around its anchor point. The Orientation and Rotation properties differ in how the layer moves when you animate them.
When you animate the Orientation property of a 3D layer, the layer turns as directly as possible to reach the specified orientation. When you animate any of the X, Y, or Z Rotation properties, the layer rotates along each individual axis according to the individual property values. In other words, Orientation values specify an angular destination, whereas Rotation values specify an angular route. Animate Rotation properties to make a layer turn multiple times.
Animating the Orientation property is often better for natural, smooth motion, whereas animating the Rotation properties provides more precise control.
Rotate or orient a 3D layer in the Composition panel
-
Select the 3D layer that you want to turn.
-
Select the Rotation tool, and select Orientation or Rotation from the Set menu to determine whether the tool affects Orientation or Rotation properties.
Choose between Orientation and Rotation to adjust the positioning or rotation of an object, layer, or camera within a composition. Choose between Orientation and Rotation to adjust the positioning or rotation of an object, layer, or camera within a composition. -
In the Composition panel, do one of the following:
- Drag the arrowhead of the 3D axis layer control corresponding to the axis around which you want to turn the layer.
- Drag a layer handle. Dragging a corner handle turns the layer around the z axis; dragging a left or right center handle turns the layer around the y axis; dragging a top or bottom handle turns the layer around the x axis.
- Drag the layer.
NoteShift-drag to constrain your manipulations to 15-degree increments.
Rotate or orient a 3D layer in the Timeline panel
-
Select the 3D layer that you want to turn.
-
In the Timeline panel, modify the Rotation or Orientation property values.
TipUse the keyboard shortcut R to show Rotation and Orientation properties.
Axis modes
Axis modes specify on which set of axes a 3D layer is transformed. Select a mode in the Tools panel.


Local Axis mode
Aligns the axes to the surface of a 3D layer.
World Axis mode
Aligns the axes to the absolute coordinates of the composition. Regardless of the rotations you perform on a layer, the axes always represent 3D space relative to the 3D world.
View Axis mode
Aligns the axes to the view you have selected. For example, suppose that a layer has been rotated and the view changed to a custom view; any subsequent transformation made to that layer while in View Axis mode happens along the axes corresponding to the direction from which you are looking at the layer.
Differences between the axis modes are only relevant when you have a 3D camera in a composition.
- The Camera tools always adjust along the local axes of the view, so the action of the Camera tools is not affected by the axis modes.
- The Tools panel remembers the last-used 3D axis mode when you quit and restart After Effects.
3D layer interactions, render order, and collapsed transformations
The positions of certain kinds of layers in the layer stacking order in the Timeline panel prevent groups of 3D layers from being processed together to determine intersections and shadows.
A shadow cast by a 3D layer does not affect a 2D layer or any layer that is on the other side of the 2D layer in the layer stacking order. Similarly, a 3D layer does not intersect with a 2D layer or any layer that is on the other side of the 2D layer in the layer stacking order. No such restriction exists for lights.
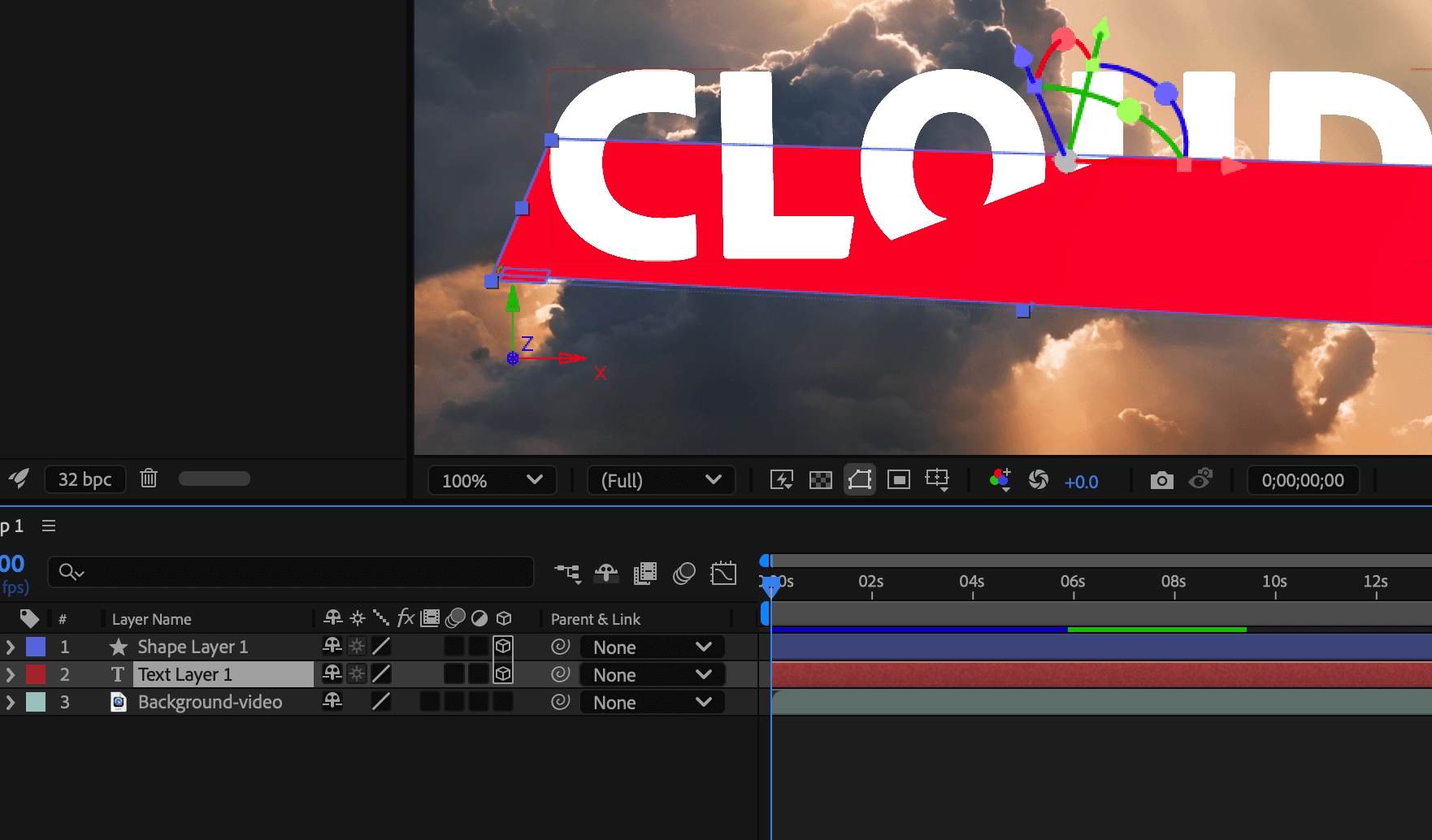
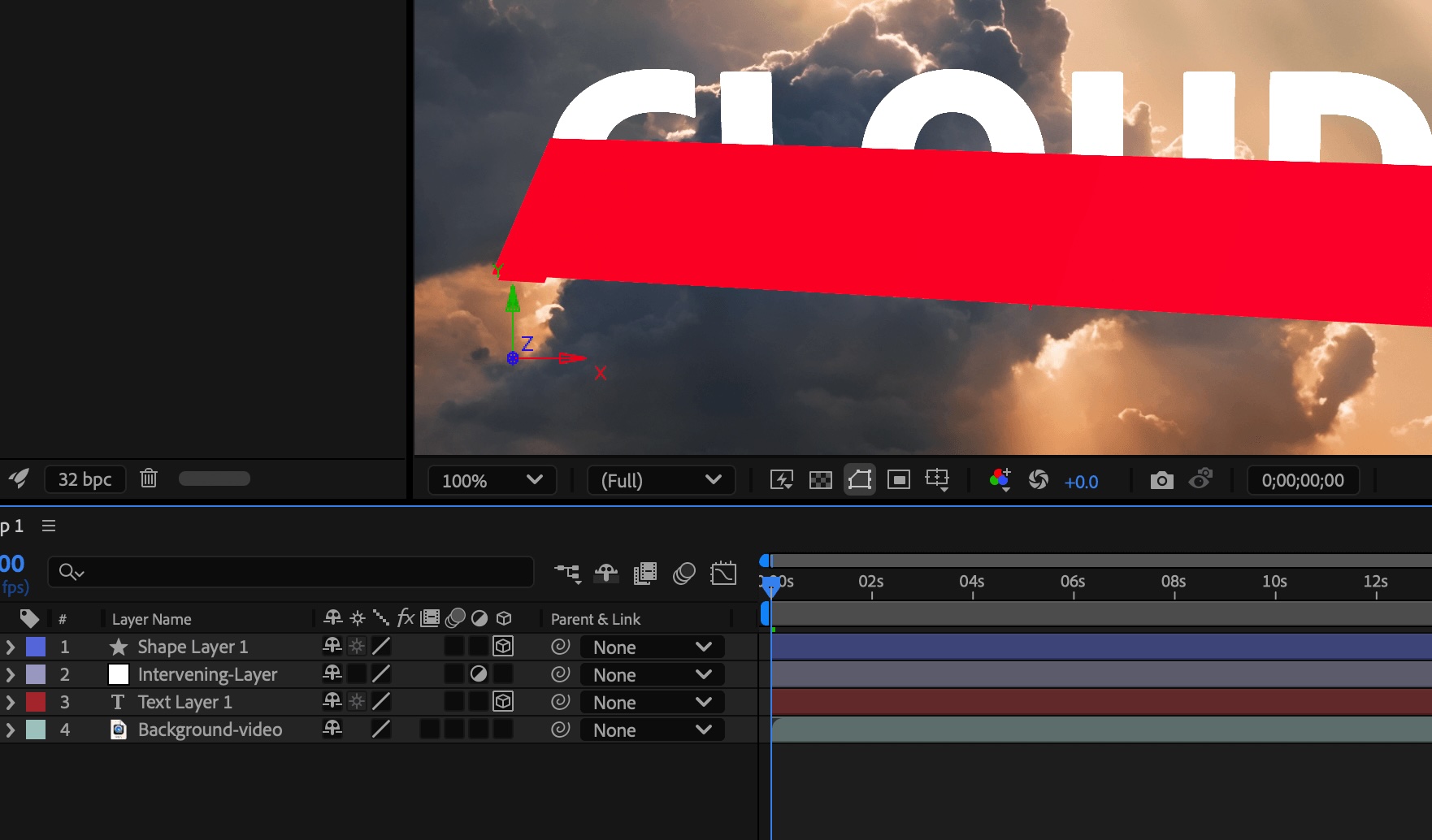
An example demonstrates how the addition of an intervening 2D layer prevents the intersection of three 3D layers.
Just like 2D layers, other types of layers also prevent 3D layers on either side from intersecting or casting shadows on one another:
An adjustment layer
A 3D layer with a layer style applied
A 3D precomposition layer to which an effect, closed mask (with mask mode other than None), or track matte has been applied
A 3D precomposition layer without collapsed transformations
A precomposition with collapsed transformations (Collapse Transformations switch ![]() selected) does not interfere with the interaction of 3D layers on either side—as long as all of the layers in the precomposition are themselves 3D layers. Collapsing transformations exposes the 3D properties of the layers that compose the precomposition. Essentially, collapsing transformations in this case allows each 3D layer to be composited into the main composition individually, rather than creating a single 2D composite for the precomposition layer and compositing that into the main composition. The tradeoff is that this setting removes your ability to specify certain layer settings for the precomposition as a whole—such as blending mode, quality, and motion blur.
selected) does not interfere with the interaction of 3D layers on either side—as long as all of the layers in the precomposition are themselves 3D layers. Collapsing transformations exposes the 3D properties of the layers that compose the precomposition. Essentially, collapsing transformations in this case allows each 3D layer to be composited into the main composition individually, rather than creating a single 2D composite for the precomposition layer and compositing that into the main composition. The tradeoff is that this setting removes your ability to specify certain layer settings for the precomposition as a whole—such as blending mode, quality, and motion blur.
Shadows cast by continuously rasterized 3D layers (including text layers) are not affected by effects applied to that layer. If you want the shadow to show the results of the effect, then precompose the layer with the effect.
To ensure that the shadow remains where expected on a 3D layer with a track matte, precompose the 3D layer and the track matte layer together (but don’t collapse transformations), and then apply the shadow to the precomposition.
Effects on continuously rasterized vector layers with 3D properties are rendered in 2D and then projected onto the 3D layer. This projection does not occur for compositions with collapsed transformations.