- What's new
-
Get started
-
Technical requirements
- Adobe Premiere technical requirements
- GPU and GPU Driver requirements
- Storage recommendations
- Processor, memory, and GPU recommendations
- Hardware-accelerated decoding and encoding
- Enable hardware accelerated decoding support
- Supported codecs and drivers for hardware-accelerated decoding
- Enable Hardware Encoding in Premiere
- Install macOS updates for Apple Metal GPU Acceleration
- Enable Mercury Playback Engine (GPU accelerated) renderer
- Adobe Premiere 25.x technical requirements
- Adobe Premiere 24.x technical requirements
- Download and install
-
Preferences and settings
- Preferences overview
- General preferences
- Set Appearance preferences
- AI Models preferences
- Audio preferences
- Audio Hardware preferences
- Auto Save preferences
- Collaboration preferences
- Color preferences
- Control Surface preferences
- Graphics preferences
- Labels preferences
- Media preferences
- Media Analysis & Transcription preferences
- Memory preferences
- Playback preferences
- Timeline preferences
- Trim preferences
- Display video on a second monitor
- Best practices for film and TV productions
- Display Premiere interface on a second monitor
- Set up accessibility features
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Set up Directx HDR for Windows
- Use touch and gesture controls
- Workflows, workspaces, and panels
-
Customize the Project panel
- Customization options for the Project panel
- Customize the Icon View in Project panel
- Customize metadata in Freeform View in Project panel
- Customize Freeform view in Project panel
- Customize List View in Project panel
- Align and reset clips to grid in Freeform View in Project panel
- Create layouts in Freeform View in Project panel
- Customize the position of the Project panel
- List View columns
- Restore or delete layouts in Freeform View in Project panel
-
Source and Program Monitor adjustments
- Overview of Source Monitor and Program Monitor
- Set display quality for Source and Program Monitors
- Adjust magnification for Source and Program Monitors
- Enable High Quality Playback
- Choose a display mode
- Gang Source and Program Monitor
- Set display options for interlaced footage
- Compare edits to clips in the Program Monitor
- Open or clear a clip in the Source Monitor
- Navigate clips in the Source menu in the Source Monitor
- Display controls in the Source and Program Monitors
- Time controls in the Source and Program Monitors
- View safe zones in the monitors
- Change the unit of measurement
- Add or remove guides
- Snap objects to guides
- Nudge clips in Program Monitor
- Save, export, and import custom guides
- Enable Dropped Frame Indicator
-
Technical requirements
-
Organize media
- Create projects
-
Import files
- Import still images
- Import images as an image sequence
- Import Photoshop and Illustrator files
- Resize imported images
- Import a Premiere Elements project
- Record audio
- Record a voice-over on an audio track from the Timeline
- Record audio using the Audio Track Mixer
- Mute input during recording
- Supported file formats
- Blackmagic RAW support
- Import media from Firefly to Premiere on desktop
- Import media from Firefly Boards to Premiere on desktop
-
Organize files
- Overview of bins
- Add and delete bins
- Open and close bins
- Manage bins
- Change bin behaviors
- Sort and view bins
- Search for media using media intelligence
- Locate and link offline files
- Relink offline media automatically
- Manually locate and relink offline media
- Consolidate duplicate folders
- Search for audio using media intelligence
- Search for similar visuals using media intelligence
-
Apply labeling
- Overview of markers
- Add a marker to a clip
- Copy and paste sequence markers
- Find, move, and delete markers
- Set default marker colors
- Show or hide markers by color
- View and edit marker properties
- Share markers with After Effects
- Overview of timecode
- Enter timecode
- View Sequence Timecode
- Choose timecode display format
- View source timecode in the Program Monitor
- Change timecode display format
- Timecode display options
- Set clip timecode manually
- Label colors in sequence tabs
- Transfer files
- Ingest proxy workflow
-
Edit projects
-
Intro to editing
- Add or remove clips
- Aspect ratios
- Set the aspect ratio of a sequence
- Pixel aspect ratio
- Frame aspect ratio
- Aspect ratio preservation
- Correct aspect ratio misinterpretations
- Convert a subclip to a Source clip
- Add media to the timeline using Source Patching
- Work with clips on the timeline using Track Targeting
- Create a subclip from the Project panel
- Create a subclip from the Timeline
- Adjust media start and end times of a subclip
- Apply Multi Transitions across audio and video clips
- Use built-in Adobe Stock panel
-
Edit video using Text-based editing
- Overview of Text-Based editing
- Add clips to the timeline using Text-Based Editing
- Transcribe video
- Edit transcripts using Text-Based Editing
- Detect and delete pauses in transcripts
- Transcribe individual source files
- Edit speaker names in transcription
- Edit sequences using Text-Based Editing
- Remove all instances of one speaker in transcript
- Multichannel audio support in Text-Based Editing
- Trim clips
-
Change clip speed
- Different ways to change clip speed and duration
- Change clip speed and duration using the Speed/Duration command
- Change clip speed and duration using the Rate Stretch tool
- Change clip speed and duration using Time Remapping
- Apply Time Interpolation Methods to adjust clip speed
- Remove Time Remapping from a clip
-
Change clip sequence
- Create a sequence
- Navigation controls in the timeline
- Navigate sequences in the timeline
- Change sequence settings
- Sequence settings reference
- Sequence presets and settings
- Create a custom sequence preset
- Copy and paste clips
- Different ways to move clips
- Rearrange clips on the timeline
- Add tracks
- Delete tracks
- Rename tracks
- Lift and paste frames
- Edit track appearance
- Sync Lock to prevent changes
- Track Lock to prevent changes
- Modify clip properties
- Set up multi-camera sequences for editing
- Compare edits to source clips
- Correct mistakes
-
Edit VR content
- VR auto-detection
- Interpret VR footage
- Assign VR properties to sequences
- 360-degree panning
- VR assignments
- Hide VR video view controls
- Immersive video effects and transitions
- Three-axis video rotation
- Assembling Ambisonics Audio
- Monitor Ambisonics audio
- Restage correctly aligned video and audio
- Publish VR videos
- VR editing in Premiere
- Edit with Generative AI
-
Intro to editing
-
Add text and images
-
Use Motion Graphics templates
- Overview of Motion Graphics templates
- Install Motion Graphics templates
- Add Motion Graphic templates to a sequence
- Organize Motion Graphics templates
- Browse and sort Motion Graphics templates
- Customize Motion Graphics templates
- Use Motion Graphics templates from Adobe Stock
- Use data-driven Motion Graphics templates
-
Stylize text
- Create titles
- Create text styles
- Apply styles to a sub-selection of the text
- Style parameters when applying from the style browser
- Replace fonts
- Create Linked and Track Styles
- Apply Linked and Track Styles
- Redefine Linked and Track Styles
- Parameters when applying as a Linked style or Track style
- Use color fonts
- Use emojis
-
Insert images and graphics
- Create responsive graphics
- Preserve intro and outro animations while creating Responsive Design graphics
- Group text and graphic layers
- Create clip layers
- Create credit rolls
- Add gradients
- Animate layers using the Effect Controls panel
- Animate layers using the Properties panel
- Rename layers
- Export graphic as a Motion Graphics template
- Create Source Graphics
- Draw objects
- Align and distribute objects
-
Insert captions
- Captions overview
- Auto transcribe video using Speech-to-Text
- Find and replace text in transcript
- Create captions
- Create styles for captions
- Translate captions
- Languages supported by Speech-to-Text
- Supported file formats for captions
- Import caption file from third-party service
- Download language packs from Creative Cloud
- Deploy language packs for Teams and Enterprise users
- Download language packs from within Premiere
-
Use Motion Graphics templates
-
Add video effects
- Types of effects
- Apply video effects
-
Effects and transitions library
- List of Video transitions
- List of Video Dissolve transitions
- Adjust effects
- Blur and Sharpen effects
- Channel effects
- Color Correction effects
- Distort effects
- Generate effects
- Image Control effects
- Immersive Video effects
- Keying effects
- Apply and customize Chromakey using the Ultra Key effect
- Ultra Key effect parameters
- Noise and Grain effects
- Perspective effects
- Stylize effects
- Time effects
- Transform effects
- Transition effects
- Utility effects
- Video effects
- Effects and transitions reorganization
- List of effects and transitions
-
Control effects and transitions using keyframes
- Adjust effect speed
- About keyframes
- Add keyframes
- Select keyframes
- Copy and paste keyframes
- Set keyframes to snap
- Delete keyframes
- Keyframes and graphs in panels
- Edit keyframes graphs
- View keyframes and properties in the Timeline panel
- View keyframes in the Effect Controls panel
- Move the Current Time Indicator to a keyframe
- Control effect changes using keyframe interpolation
- Change the keyframe interpolation method
- Filter properties in the Effect Controls panel
- Adjust or reset controls in the Effect Controls panel
- Control change using Bezier keyframe interpolation
- Create masks and composites
-
Commonly used effects
- Auto Reframe overview
- Add Auto Reframe effect to sequences
- Add Auto Reframe effect to clips
- Apply Motion effect
- Edit vector graphics using Vector Motion effect
- Stabilize shaky footage using Warp Stabilizer
- Warp Stabilizer settings
- Create fade-in video effects
- Add lightning effects
- Create a Jacob’s ladder effect
- Effects and transitions removed from Adobe Premiere
-
Apply video transitions
- Transitions overview
- Set and apply default transitions
- Apply single-sided transitions
- Copy and paste transitions
- Align and reposition transitions
- Reposition the center of a transition
- Change transition settings
- Replace transitions
- Move cuts and transitions simultaneously
- Change transition duration using the Effect Controls panel
- Morph Cut overview
- Apply morph cut to smoothen jump cuts
- Morph Cut transition options
- Clip handles settings
- Video transitions using clip handles
-
Work with masks
- Redesigned Rectangle, Ellipse, and Pen tools
- Object masking in Premiere
- Create masks using shapes
- Refining and combining masks
- Apply effects to existing unassigned masks in Premiere
- Copy, paste or move masks
- Adjust mask properties
- Mask tracking tools in Premiere
- Adjust masks at the clip or frame level in Premiere
- Track masks
- Masking tool actions and modifiers
- Work with composites
-
Add audio effects
-
Basic audio editing
- Audio editing concepts
- Extract audio from clips
- Link audio and video clips
- Synchronize audio and video
- Synchronize clips in the Timeline panel
- Merge clips in the Project panel
- Merge clips in the Timeline panel
- Use the timecode from an audio primary clip to create a merged clip
- Edit merged clips
- Edit metadata of merged clips
- Limitations of merged clips
- View audio and video waveforms in the Source Monitor
-
Advanced audio techniques
- Audio channel mapping
- Audio Track Mixer overview
- Create a submix
- Map source audio channels on import
- Change source audio channel mapping
- Map to audio output device hardware channels
- Break a stereo track into mono tracks
- Use mono clips as stereo clips
- Edit a multi-clip link in the Source Monitor
- Clean audio with bulk mute or bleep
-
Adjust volume and levels
- Automatically tag audio
- Apply Enhance Speech
- Audio editing with Essential Sound panel
- Improve dialogue clarity
- Repair dialogue
- Create a Reverb effect
- Automatically duck audio
- Create audio presets
- Adjust gain in audio
- Adjust track volume
- Auto-match audio loudness
- Monitor volume levels
- Use Dynamic Audio Waveforms
- Enhance Speech technical requirements
- Live waveform editing
- Global mute in Premiere (beta)
- Apply audio effects
- Apply audio transitions
- Use Adobe Stock audio
-
Basic audio editing
-
Correct color
- Color correction fundamentals
- Add color effects
-
Set up Color Management
- Color Management overview
- How Color Management works
- Color Management and Lumetri Color
- Color Management options
- Manage source media colors in the Program Monitor
- Configure sequence Color Management
- Configure clips for Color Management using Clip Modify
- Customize color presets for new or existing sequences
- Configure sequence’s output color space
- Disable Color Management
- Premiere and After Effects Color Management compatibility
- Tone mapping in Premiere
-
Render and export
- Render sequences for playback
-
Export files
- Export video
- Export a still frame
- Export a still image
- Export transcripts
- Export caption tracks
- Export selected captions
- Export text from Motion Graphics
- Best practices for exporting video for social media and phones
- Export videos for social media channels
- Export a project as an EDL file
- Export a project as a Final Cut Pro XML file
- Export videos with Content Credentials
- Stream video
-
Collaborate with others
-
Collaborate using Team Projects
- About Team Projects
- When to use Team Projects and when to use Productions
- Collaboration using Team Projects
- Create Team Projects
- Create linked Team Projects
- Add media
- Manage media
- Connect to Team Projects service
- Invite collaborators to existing Team Projects
- Accept an invitation to collaborate
- View online collaborators
- Remove collaborators from Team Projects
- Search and filter Team Projects
- Archive Team Projects
- Delete archived Team Projects
- Restore archived Team Projects
- Publish an edited sequence with changes
- Visual cues during collaboration
- Offline editing and cloud sync status
- View versions of a Team Project
- Create a new Team Project from a version
- Specify Auto Save cache location
- Sequence Locking
- Sequence Locking for offline editing
- View auto saves
- Convert Premiere projects to Team Projects
- Share for review using Frame.io
-
Collaborate using Team Projects
- Use Premiere Pro with other apps
-
Troubleshooting
- Limitations and known issues
- Media issues
- Crash issues
- Preferences and settings issues
- Export issues
- Audio issues
-
Playback issues
- Timeline doesn’t show video preview
- Not able to optimize playback performance
- Hardware setup not optimal for playback performance
- Audio playback keep getting stuck
- Optimize playback performance for H.264 and H.265 media
- Troubleshoot sequence and file-interpretation settings
- Choppy playback and poor performance issue
- Slow rendering and playback
- Use Premiere with other apps
Correct color using RGB curves
Learn how to use RGB Curves to make quick and precise color adjustments to achieve natural-looking results.
Curves feature allows you to make quick and precise color adjustments using two types of curves—RGB Curves and Hue Saturation Curves.
RGB Curves
You can edit curves using two approaches:
- Using the RGB Curves available in the Lumetri Color panel.
- Using the RGB Curves effect available in the Effect Controls panel.

A. Curves settings that you can adjust in the Effect Controls panel B. Curves settings that you can adjust in the Lumetri Color panel

Adjust luma and tonal ranges using control points
RGB Curves let you adjust luma and tonal ranges across the clip using curves. The master curve controls the Luma. Initially, the master curve is represented as a straight white diagonal line. Adjusting the master curve adjusts the values of all three RGB channels simultaneously.


Some common ways you can manipulate control points
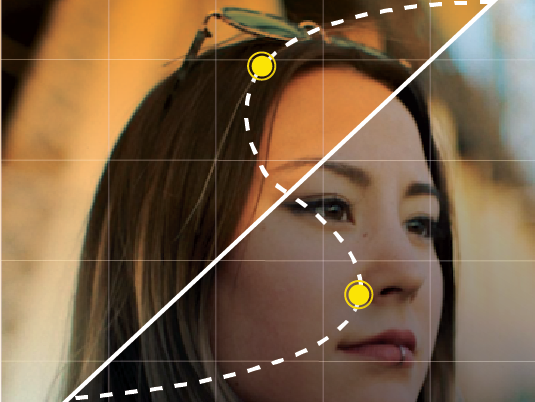
To add highlights, drag a control point to the upper-right area of the line. To add shadows, drag a control point to the lower-left area.
Selectively adjust tonal values for RGB channels. To adjust different tonal areas, add control points directly to the curve.
To lighten or darken the tonal area, drag a control point up or down. To increase or decrease the contrast, drag a control point left or right.
To delete a control point, press Ctrl (Windows) or command (macOS) and select the control point.


You can add warm tones to a video clip using the RGB Curves. In this example, the white and red lines are used to increase the warm tones in the clip. The blue and green lines are used to decrease the presence of blues and greens in the clip. A reddish tint is added to the clip, making it appear warmer.
Add natural-looking contrast using S curves


You can edit an image's contrast using RGB Curves. In this example, an S curve enhances the contrast, making the guy look less pale. The blue color of the sky also appears brighter.
Craft the perfect story with Premiere
Find the best-in-class video-editing tools all in one place.