Open the Property inspector (Window > Properties), if it isn’t already open and select the CSS option in the left corner of the panel.
- Dreamweaver User Guide
- Introduction
- Dreamweaver and Creative Cloud
- Dreamweaver workspaces and views
- Set up sites
- About Dreamweaver sites
- Set up a local version of your site
- Connect to a publishing server
- Set up a testing server
- Import and export Dreamweaver site settings
- Bring existing websites from a remote server to your local site root
- Accessibility features in Dreamweaver
- Advanced settings
- Set site preferences for transferring files
- Specify proxy server settings in Dreamweaver
- Synchronize Dreamweaver settings with Creative Cloud
- Using Git in Dreamweaver
- Manage files
- Create and open files
- Manage files and folders
- Getting and putting files to and from your server
- Check in and check out files
- Synchronize files
- Compare files for differences
- Cloak files and folders in your Dreamweaver site
- Enable Design Notes for Dreamweaver sites
- Preventing potential Gatekeeper exploit
- Layout and design
- CSS
- Understand Cascading Style Sheets
- Laying out pages using CSS Designer
- Using CSS preprocessors in Dreamweaver
- How to set CSS Style preferences in Dreamweaver
- Move CSS rules in Dreamweaver
- Convert inline CSS to a CSS rule in Dreamweaver
- Work with div tags
- Apply gradients to background
- Create and edit CSS3 transition effects in Dreamweaver
- Format code
- Page content and assets
- Set page properties
- Set CSS heading properties and CSS link properties
- Work with text
- Find and replace text, tags, and attributes
- DOM panel
- Edit in Live View
- Encoding documents in Dreamweaver
- Select and view elements in the Document window
- Set text properties in the Property inspector
- Spell check a web page
- Using horizontal rules in Dreamweaver
- Add and modify font combinations in Dreamweaver
- Work with assets
- Insert and update dates in Dreamweaver
- Create and manage favorite assets in Dreamweaver
- Insert and edit images in Dreamweaver
- Add media objects
- Adding videos in Dreamweaver
- Insert HTML5 video
- Insert SWF files
- Add audio effects
- Insert HTML5 audio in Dreamweaver
- Work with library items
- Using Arabic and Hebrew text in Dreamweaver
- Linking and navigation
- jQuery widgets and effects
- Coding websites
- About coding in Dreamweaver
- Coding environment in Dreamweaver
- Set coding preferences
- Customize code coloring
- Write and edit code
- Code hinting and code completion
- Collapse and expand code
- Reuse code with snippets
- Lint code
- Optimize code
- Edit code in Design view
- Work with head content for pages
- Insert server-side includes in Dreamweaver
- Using tag libraries in Dreamweaver
- Importing custom tags into Dreamweaver
- Use JavaScript behaviors (general instructions)
- Apply built-in JavaScript behaviors
- About XML and XSLT
- Perform server-side XSL transformations in Dreamweaver
- Performing client-side XSL transformations in Dreamweaver
- Add character entities for XSLT in Dreamweaver
- Format code
- Cross-product workflows
- Installing and using extensions to Dreamweaver
- In-App updates in Dreamweaver
- Insert Microsoft Office documents in Dreamweaver (Windows only)
- Working with Fireworks and Dreamweaver
- Edit content in Dreamweaver sites using Contribute
- Dreamweaver-Business Catalyst integration
- Create personalized email campaigns
- Templates
- About Dreamweaver templates
- Recognizing templates and template-based documents
- Create a Dreamweaver template
- Create editable regions in templates
- Create repeating regions and tables in Dreamweaver
- Use optional regions in templates
- Define editable tag attributes in Dreamweaver
- How to create nested templates in Dreamweaver
- Edit, update, and delete templates
- Export and import xml content in Dreamweaver
- Apply or remove a template from an existing document
- Edit content in Dreamweaver templates
- Syntax rules for template tags in Dreamweaver
- Set highlighting preferences for template regions
- Benefits of using templates in Dreamweaver
- Mobile and multiscreen
- Dynamic sites, pages and web forms
- Understand web applications
- Set up your computer for application development
- Troubleshoot database connections
- Removing connection scripts in Dreamweaver
- Design dynamic pages
- Dynamic content sources overview
- Define sources of dynamic content
- Add dynamic content to pages
- Changing dynamic content in Dreamweaver
- Display database records
- Provide and troubleshoot live data in Dreamweaver
- Add custom server behaviors in Dreamweaver
- Building forms using Dreamweaver
- Use forms to collect information from users
- Create and enable ColdFusion forms in Dreamweaver
- Create web forms
- Enhanced HTML5 support for form elements
- Develop a form using Dreamweaver
- Building applications visually
- Build master and detail pages in Dreamweaver
- Build search and results pages
- Build a record insert page
- Build an update record page in Dreamweaver
- Building record delete pages in Dreamweaver
- Use ASP commands to modify database in Dreamweaver
- Build a registration page
- Build a login page
- Build a page that only authorized users can access
- Securing folders in Coldfusion using Dreamweaver
- Using ColdFusion components in Dreamweaver
- Test, preview, and publish websites
- Troubleshooting
Learn how to use the text Property Inspector to apply HTML formatting or CSS formatting in Dreamweaver.
You can use the text Property inspector to apply HTML formatting or Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) formatting. When you apply HTML formatting, Dreamweaver adds properties to the HTML code in the body of your page. When you apply CSS formatting, Dreamweaver writes properties to the head of the document or to a separate style sheet.
When you create CSS inline styles, Dreamweaver adds style attribute code directly to the body of the page.
About formatting text (CSS versus HTML)
Formatting text in Dreamweaver is similar to using a standard word processor. You can set default formatting styles (Paragraph, Heading 1, Heading 2, and so on) for a block of text, change the font, size, color, and alignment of selected text, or apply text styles such as bold, italic, code (monospace), and underline.
Dreamweaver has two Property inspectors, integrated into one: the CSS Property inspector and the HTML Property inspector. When you use the CSS Property inspector, Dreamweaver formats text using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). CSS gives web designers and developers greater control over web page design, while providing improved features for accessibility and reduced file size. The CSS Property inspector lets you access existing styles, as well as create new ones.
Using CSS is a way to control the style of a web page without compromising its structure. By separating visual design elements (fonts, colors, margins, and so on) from the structural logic of a web page, CSS gives web designers visual and typographic control without sacrificing the integrity of the content. In addition, defining typographic design and page layout from within a single, distinct block of code—without having to resort to image maps, font tags, tables, and spacer GIFs—allows for faster downloads, streamlined site maintenance, and a central point from which to control design attributes across multiple web pages.
You can store styles created with CSS directly in the document, or for more power and flexibility, you can store styles in an external style sheet. If you attach an external style sheet to several web pages, all the pages automatically reflect any changes you make to the style sheet. To access all CSS rules for a page, use the CSS Styles panel (Window > CSS Styles). To access rules that apply to a current selection, use the CSS Styles panel (Current mode) or the Targeted Rule pop-up menu in the CSS Property inspector.
If you prefer, you can use HTML markup tags to format text in your web pages. To use HTML tags instead of CSS, format your text using the HTML Property inspector.
You can combine CSS and HTML 3.2 formatting within the same page. Formatting is applied in a hierarchical manner: HTML 3.2 formatting overrides formatting applied by external CSS style sheets, and CSS embedded in a document overrides external CSS.
Edit CSS rules in the Property inspector
-
-
Do one of the following:
- Place the insertion point inside a block of text that’s been formatted by a rule you want to edit. The rule appears in the Targeted Rule pop-up menu.
- Select a rule from the Targeted Rule pop-up menu.
- Click Edit Rule.
Select a rule from the Targeted Rule pop-up menu. 
Select a rule from the Targeted Rule pop-up menu. -
Make changes to the rule by using the various options in the CSS Property inspector.
Targeted Rule
Is the rule you are editing in the CSS Property inspector. When you have an existing style applied to text, the rule affecting the text’s format appears when you click inside the text on the page. You can also use the Targeted Rule pop-up menu to create new CSS rules, new in-line styles, or apply existing classes to selected text. If you’re creating a new rule, you’ll need to complete the New CSS Rule dialog box. For more information, see the links at the end of this topic.
Edit Rule
Opens the CSS Rule Definition dialog box for the targeted rule. If you select New CSS Rule from the Targeted Rule pop-up menu and click the Edit Rule button, Dreamweaver opens the New CSS Rule definition dialog box instead.
CSS Designer
Opens the CSS Designer panel and displays properties for the targeted rule in Current view.
Font
Changes the font of the targeted rule.
Size
Sets the font size for the targeted rule.
Text Color
Sets the selected color as the font color in the targeted rule. Select a web-safe color by clicking the color box, or enter a hexadecimal value (for example, #BB5153) in the adjacent text field.
Edit CSS rules using the Edit Rule option. 
Edit CSS rules using the Edit Rule option. Bold
Adds the bold property to the targeted rule.
Italic
Adds the italics property to the targeted rule.
Left, Center, and Right Align
Aligns the targeted rule to the left, center, or right.
NoteThe Font, Size, Text Color, Bold, Italic, and Alignment properties always display the properties for the rule that applies to the current selection in the Document window. When you change any of these properties, you affect the targeted rule.
Edit text color using Property inspector
If you have not applied any specific rule for your text, you can edit the color of your text directly from the Property Inspector. In the following example, note the color of the text before editing. The field adjacent to the color picker displays white, indicating the color of the text where you have placed your cursor.

To edit the color of the text, select the text that you want to edit. Click the color picker and select any color of your choice. See the following image where the property inspector displays the new color.

Set HTML formatting in the Property inspector
-
Open the Property inspector (Window > Properties), if it isn’t already open, and click the HTML button.
-
Select the text that you want to format.
-
Set the options you want to apply to the selected text:
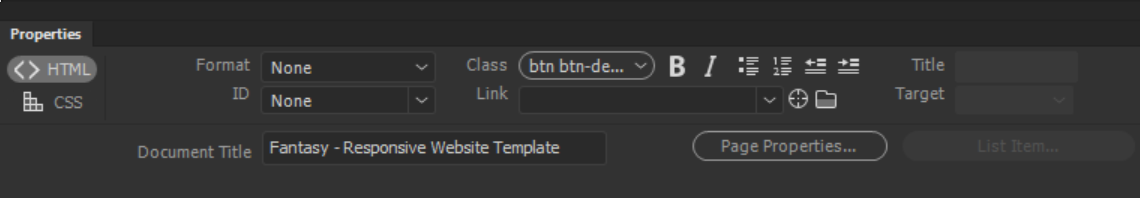
Set HTML formatting text properties 
Set HTML formatting text properties Format
Sets the paragraph style of the selected text. Paragraph applies the default format for a <p> tag, Heading 1 adds an H1 tag, and so on.
ID
Assigns an ID to your selection. The ID pop-up menu (if applicable) lists all of the document’s unused, declared IDs.
Class
Displays the class style that is currently applied to the selected text. If no styles have been applied to the selection, the pop‑up menu shows No CSS Style. If multiple styles have been applied to the selection, the menu is blank.
Use the Style menu to do any of the following:
Select the style you want to apply to the selection.
Select None to remove the currently selected style.
Select Rename to rename the style.
Select Attach Style Sheet to open a dialog box that lets you attach an external style sheet to the page.
Bold
Applies either <b> or <strong> to the selected text according to the style preference set in the General category of the Preferences dialog box.
Italic
Applies either <i> or <em> to the selected text according to the style preference set in the General category of the Preferences dialog box.
Unordered List
Creates a bulleted list of the selected text. If no text is selected, a new bulleted list is started.
Ordered List
Creates a numbered list of the selected text. If no text is selected, a new numbered list is started.
Blockquote and Remove Blockquote
Indent or remove indentation from the selected text by applying or removing the blockquote tag. In a list, indenting creates a nested list and removing the indentation unnests the list.
Link
Creates a hypertext link of the selected text. Click the folder icon to browse to a file in your site; type the URL; drag the Point-To-File icon to a file in the Files panel; or drag a file from the Files panel into the box.
Title
Specifies the textual tooltip for a hypertext link.
Target
Specifies the frame or window in which the linked document will load:
_blank loads the linked file in a new, unnamed browser window.
_parent loads the linked file in the parent frameset or window of the frame that contains the link. If the frame containing the link is not nested, the linked file loads into the full browser window.
_self loads the linked file in the same frame or window as the link. This target is implied, so you generally don’t need to specify it.
_top loads the linked file in the full browser window, thereby removing all frames.
Rename a class from the HTML Property inspector
Dreamweaver displays all of the classes available to your page in the Class menu of the HTML Property inspector. You can rename styles in this list by selecting the Rename option at the end of the list of class styles.
-
From the Property inspector panel, select the Class drop-down list.
-
From the list that pops up, select Rename at the end of the list.
-
Select the style that you want to rename from the Rename Style pop‑up menu.
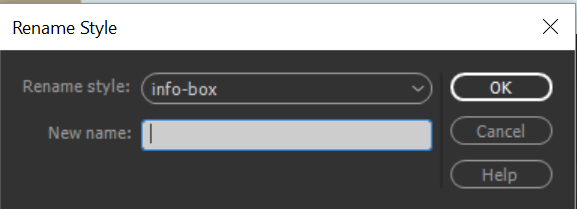
Rename an HTML class 
Rename an HTML class -
Enter a new name in the New Name text field and click OK.