- Acrobat User Guide
- Introduction to Acrobat
- Access Acrobat from desktop, mobile, web
- Introducing the new Acrobat experience
- What's new in Acrobat
- Keyboard shortcuts
- System Requirements
- Download Adobe Acrobat
- Download Acrobat | Enterprise term or VIP license
- Download Acrobat 64-bit for Windows
- Install Adobe Acrobat Reader | Windows
- Install Adobe Acrobat Reader | Mac OS
- Install updates for Acrobat and Reader
- Update your Acrobat to the latest version
- Download Acrobat 2020
- Release Notes | Acrobat, Reader
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Opening and viewing PDFs
- Working with online storage accounts
- Acrobat and macOS
- Acrobat notifications
- Grids, guides, and measurements in PDFs
- Asian, Cyrillic, and right-to-left text in PDFs
- Adobe Acrobat for Outlook
- Set Acrobat as default PDF viewer
- Explore Acrobat tools
- Workspace basics
- Creating PDFs
- Editing PDFs
- Edit text in PDFs
- Edit images or objects in a PDF
- Rotate, move, delete, and renumber PDF pages
- Edit scanned PDFs
- Enhance document photos captured using a mobile camera
- Optimizing PDFs
- PDF properties and metadata
- Links and attachments in PDFs
- PDF layers
- Page thumbnails and bookmarks in PDFs
- PDFs converted to web pages
- Setting up PDFs for a presentation
- PDF articles
- Geospatial PDFs
- Applying actions and scripts to PDFs
- Change the default font for adding text
- Delete pages from a PDF
- Edit a signed PDF | FAQ
- Scan and OCR
- Forms
- PDF forms basics
- Create a form from scratch in Acrobat
- Create and distribute PDF forms
- Fill in PDF forms
- PDF form field properties
- Fill and sign PDF forms
- Setting action buttons in PDF forms
- Publishing interactive PDF web forms
- PDF form field basics
- PDF barcode form fields
- Collect and manage PDF form data
- About forms tracker
- PDF forms help
- Send PDF forms to recipients using email or an internal server
- Combining files
- Combine or merge files into single PDF
- Rotate, move, delete, and renumber PDF pages
- Add headers, footers, and Bates numbering to PDFs
- Crop PDF pages
- Add watermarks to PDFs
- Add backgrounds to PDFs
- Working with component files in a PDF Portfolio
- Publish and share PDF Portfolios
- Overview of PDF Portfolios
- Create and customize PDF Portfolios
- Sharing, reviews, and commenting
- Share and track PDFs online
- Mark up text with edits
- Preparing for a PDF review
- Starting a PDF review
- Hosting shared reviews on SharePoint or Office 365 sites
- Participating in a PDF review
- Add comments to PDFs
- Adding a stamp to a PDF
- Approval workflows
- Managing comments | view, reply, print
- Importing and exporting comments
- Tracking and managing PDF reviews
- Saving and exporting PDFs
- Security
- Enhanced security setting for PDFs
- Securing PDFs with passwords
- Manage Digital IDs
- Securing PDFs with certificates
- Opening secured PDFs
- Removing sensitive content from PDFs
- Setting up security policies for PDFs
- Choosing a security method for PDFs
- Security warnings when a PDF opens
- Securing PDFs with Adobe Experience Manager
- Protected View feature for PDFs
- Overview of security in Acrobat and PDFs
- JavaScripts in PDFs as a security risk
- Attachments as security risks
- Allow or block links in PDFs
- Edit secured PDFs
- Electronic signatures
- Sign PDF documents
- Capture your signature on mobile and use it everywhere
- Send documents for e-signatures
- Create a web form
- Request e-signatures in bulk
- Collect online payments
- Brand your account
- About certificate signatures
- Certificate-based signatures
- Validating digital signatures
- Adobe Approved Trust List
- Manage trusted identities
- Printing
- Accessibility, tags, and reflow
- Searching and indexing
- Multimedia and 3D models
- Add audio, video, and interactive objects to PDFs
- Adding 3D models to PDFs (Acrobat Pro)
- Displaying 3D models in PDFs
- Interacting with 3D models
- Measuring 3D objects in PDFs
- Setting 3D views in PDFs
- Enable 3D content in PDF
- Adding multimedia to PDFs
- Commenting on 3D designs in PDFs
- Playing video, audio, and multimedia formats in PDFs
- Add comments to videos
- Print production tools (Acrobat Pro)
- Preflight (Acrobat Pro)
- PDF/X-, PDF/A-, and PDF/E-compliant files
- Preflight profiles
- Advanced preflight inspections
- Preflight reports
- Viewing preflight results, objects, and resources
- Output intents in PDFs
- Correcting problem areas with the Preflight tool
- Automating document analysis with droplets or preflight actions
- Analyzing documents with the Preflight tool
- Additional checks in the Preflight tool
- Preflight libraries
- Preflight variables
- Color management
- Troubleshoot
- Troubleshoot PDF printing in Acrobat and Acrobat Reader
- Adobe Acrobat license has either expired or not been activated
- Edit PDF forms created in LiveCycle Designer
- Insufficient data for an image error on Adobe Acrobat
- Resolve errors related to the AcroCEF/RdrCEF processes of Acrobat or Acrobat Reader
Learn how to effortlessly view and interact with 3D models in Acrobat.
With Acrobat, you can view and interact with top-notch 3D designs made in professional CAD or modeling programs and embedded in PDFs. You can hide and show parts of a 3D model, remove a cover to look inside, and rotate parts as if holding them in your hands.
Enable playing of 3D content in PDF
When you open a PDF with 3D content, a yellow bar appears at the top with the message, Multimedia and 3D content has been disabled. Enable this feature if you trust this document.
You can enable the 3D content in the document to start playing the 3D content.
To enable content, select Options on the upper right. A drop-down menu appears.
Select either Trust this document one time only or Trust this document always as per your preference.
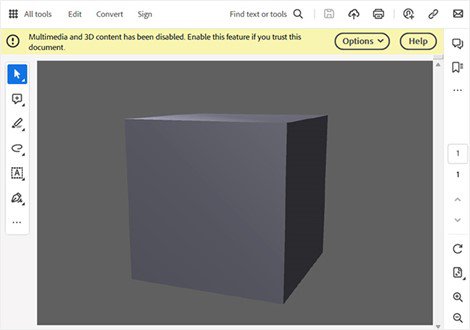

Enable 3D content permanently
-
Press Ctrl + K (Windows) or Command + K (macOS) to open Preferences.
-
Select Multimedia & 3D > Enable playing of Multimedia and 3D content checkbox.
-
Select OK.
You can learn about enabling 3D content in PDF.
Activate a 3D content in PDF
A 3D model initially appears as a two-dimensional preview image.
-
Open the PDF file containing the 3D model.
-
Select the 3D model using either the Hand or Select tool.
The 3D model is activated. A 3D toolbar appears above the model.
You can now interact or play animations in your 3D model.
3D toolbar overview
When you activate a 3D model, the 3D toolbar will appear above it. You can use this toolbar to zoom in and out, rotate, and move around the model.
To play with the 3D model, you can select and drag the different navigation tools. As you navigate the model, imagine viewing the 3D model from a camera's point of view.
To view other tools, select the drop-down option on the right of the 3D toolbar.


3D navigation tools


Rotate |
Turns 3D objects around relative to the screen. You can also use the Hand or Select tool to rotate an object. Ensure that Rotate tool is selected in the 3D toolbar. |


Spin |
Turns a 3D model in parallel to two fixed axes (x-axis and z-axis) in the 3D model. |


Pan |
Moves the model vertically and horizontally only. You can also pan with the Hand or Select tool. Press ctrl and drag. |


Zoom |
Moves you toward, or away from the objects on the screen when you drag vertically. You can also zoom with the Hand or Select tool by holding down shift key as you drag. |


Walk |
Pivots horizontally or vertically around the canvas when you drag horizontally or vertically maintaining a constant elevation level, regardless of how you drag. This tool is useful for architectural 3D models. To change the walking speed, change the default display units in Preferences > Measuring (3D) > Use Scale and Units from Model (when present). |


Fly |
Navigates through a model while maintaining the surface orientation. Selecting the model and moving the cursor moves the model closer to you. Drag the cursor right or left to turn. To rotate the camera view, click the left mouse button inside the 3D window and drag to turn the camera view. To return to the starting camera direction, move the mouse back to the initial click point. Use the mouse scroll wheel to move rapidly backward and forward along the camera view direction. This functionality is useful if you get lost within a model or fly into the surface. |


Camera Properties |
Defines the camera angle, alignment, and other properties that define the lens through which a 3D model is viewed. Camera properties are components of views but are set independently. |


3D Measurement Tool |
Measures part sizes and distances in the 3D model. |
3D toolbar view controls


Default View |
Returns to a preset zoom, pan, rotation, and projection mode of the 3D model. Use the Options menu in the View pane of the Model Tree to set a different view as the default. Or use the Manage Views command on the 3D toolbar Views menu to set a different view as the default. If an object ever moves out of your view, you have, in essence, turned your camera away from the object. Select the Default View icon on the 3D toolbar to move the object back into view. |
|
Views menu |
Lists any views defined for the current 3D model. |


Toggel Model Tree |
Opens and hides the Model Tree. The Model Tree can be used to hide or show parts of the 3D model. |




Play/Pause Animation |
Plays or pauses any JavaScript-enabled animation. The Play/Pause Animation pop-up menu opens a slider that you can drag back and forth to move to different times in the animation sequence. |


Use Orthographic/Perspective Projection |
Toggles between displaying perspective and orthographic projection of the 3D object. |


Model Render Mode |
Determines how the 3D shape appears. For an illustrated guide, see Examples of model rendering modes. |


Enable Extra Lighting |
Lists the different lighting effects that are available to enhance the illumination of the 3D object. Experiment to get the visual effects you want. |


Background Color |
Opens the color picker, which you can use to select a different color for the space surrounding the 3D object. |


Toggle Cross Section |
Shows and hides cross-sections of the object. Select the pop-up menu to open the Cross Section Properties dialog box. For more information, see Create cross sections. |
|
Add Multimedia/3D Comment |
Enables you to add a sticky note to any part of the 3D model. The note stays with the view. See Commenting on 3D designs in PDFs. |
3D Preferences
In the Preferences dialog box, the Multimedia & 3D panel allows you to manage the default display of the 3D toolbar and Model Tree. Additionally, you can specify the default renderer and decide whether animations are allowed.
Multimedia and 3D options
Enable Playing of Multimedia and 3D Content
By default, 3D content in PDFs is disabled due to potential security vulnerabilities. To enable the playing of 3D content, select the option “Enable Playing of 3D Content” in the Multimedia & 3D panel.
Renderer Options
Preferred Renderer
Specifies the appropriate rendering engine in the Multimedia & 3D preferences to affect performance and quality. You can select DirectX® or OpenGL option for faster rendering that uses the graphics chip on the video adapter. If Software is selected, rendering takes more time, but the performance is often more consistent with the model rendering of the originating application.
Enable hardware rendering for legacy video cards
Forces the use of a hardware accelerator for even video adapters that do not support a pixel shader.
Enable Double-Sided Rendering
Select this option to render both sides of the model. Deselecting this option renders only the side facing the user to save time and space.
Preferred 3D PMI Rendering Mode
Specifies the PMI mode to use for rendering. You can select one of the following options:
- Use content's setting: The rendering of the PMI uses the setting of each PMI to decide whether it uses the Z-buffer.
- Always render 3D PMI in front of model: The rendering of the PMI ignores the Z-buffer regardless of the setting in the file.
- Always render 3D PMI using Z-buffer: The rendering of the PMI always turns on Z-buffer regardless of the setting in the file.
3D Tool Options
Open Model Tree On 3D Activation
Determines whether the Model Tree is displayed when the 3D model is activated. Choose Use Annotation’s Setting to use whichever setting the author used when adding the 3D model to the PDF.
Default Toolbar State
Determines whether the 3D toolbar is shown or hidden when a 3D model is activated. Choose Use Annotation’s Setting to use whichever setting the author used when adding the 3D model to the PDF.
Enable selection for the Hand tool
Lets the user select and highlight parts of the 3D model using the Hand tool. If this option is not selected, use the Object Data tool (Tools > Interactive Objects > Select Object) to select the object.
Consolidate tools on the 3D Toolbar
Selecting this option places the manipulation and navigation tools under the Rotate tool, thereby shortening the 3D toolbar.
Enable view transitions
Some 3D models include animated transitions between views. Deselect this option if you want to prevent this 3D animation.
Show 3D orientation axis
Turns on or off an in-scene display of an axis that indicates the current orientation of the 3D scene.
Auto-Degrade Options
Optimization scheme for Low Framerate
Specifies what happens to animations of complex models when the framerate becomes low. None does not compromise the visuals and leaves the framerate low. Bounding Box shows the three-dimensional planes enclosing the parts instead of the parts themselves, which keeps the framerate high. Drop Objects does not show some parts of the model, which keeps the framerate high.
Framerate Threshold
Sets the minimum framerate, either by dragging the slider or entering a number in the value box. If the framerate drops below that number of frames per second, the Optimization Scheme For Low Framerate option goes into effect.

