To apply a Curves adjustment, do one of the following:
- Photoshop User Guide
- Introduction to Photoshop
- Photoshop and other Adobe products and services
- Photoshop on mobile (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop on the iPad (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop on the iPad | Common questions
- Get to know the workspace
- System requirements | Photoshop on the iPad
- Create, open, and export documents
- Add photos
- Work with layers
- Draw and paint with brushes
- Make selections and add masks
- Retouch your composites
- Work with adjustment layers
- Adjust the tonality of your composite with Curves
- Apply transform operations
- Crop and rotate your composites
- Rotate, pan, zoom, and reset the canvas
- Work with Type layers
- Work with Photoshop and Lightroom
- Get missing fonts in Photoshop on the iPad
- Japanese Text in Photoshop on the iPad
- Manage app settings
- Touch shortcuts and gestures
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Edit your image size
- Livestream as you create in Photoshop on the iPad
- Correct imperfections with the Healing Brush
- Create brushes in Capture and use them in Photoshop on the iPad
- Work with Camera Raw files
- Create and work with Smart Objects
- Adjust exposure in your images with Dodge and Burn
- Auto adjustment commands in Photoshop on the iPad
- Smudge areas in your images with Photoshop on the iPad
- Saturate or desaturate your images using Sponge tool
- Content aware fill for iPad
- Photoshop on the web (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop (beta) (not available in mainland China)
- Generative AI (not available in mainland China)
- Common questions on generative AI in Photoshop
- Generative Fill in Photoshop on the desktop
- Generate Image with descriptive text prompts
- Generative Expand in Photoshop on the desktop
- Replace background with Generate background
- Get new variations with Generate Similar
- Select an AI model for generative control
- Generative Fill in Photoshop on the iPad
- Generative Expand in Photoshop on the iPad
- Generative AI features in Photoshop on the web
- Content authenticity (not available in mainland China)
- Cloud documents (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop cloud documents | Common questions
- Photoshop cloud documents | Workflow questions
- Manage and work with cloud documents in Photoshop
- Upgrade cloud storage for Photoshop
- Unable to create or save a cloud document
- Solve Photoshop cloud document errors
- Collect cloud document sync logs
- Invite others to edit your cloud documents
- Share documents for review
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Preferences
- Learn faster with the Photoshop Discover Panel
- Create documents
- Place files
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Customize keyboard shortcuts
- Tool galleries
- Performance preferences
- Contextual Task Bar
- Use tools
- Presets
- Grid and guides
- Touch gestures
- Use the Touch Bar with Photoshop
- Touch capabilities and customizable workspaces
- Technology previews
- Metadata and notes
- Place Photoshop images in other applications
- Rulers
- Show or hide non-printing Extras
- Specify columns for an image
- Undo and history
- Panels and menus
- Position elements with snapping
- Position with the Ruler tool
- Organize, share, and collaborate with Projects
- Refine Adobe Firefly generations
- Image and color basics
- How to resize images
- Work with raster and vector images
- Image size and resolution
- Acquire images from cameras and scanners
- Create, open, and import images
- View images
- Invalid JPEG Marker error | Opening images
- Viewing multiple images
- Customize color pickers and swatches
- High dynamic range images
- Match colors in your image
- Convert between color modes
- Color modes
- Erase parts of an image
- Blending modes
- Choose colors
- Customize indexed color tables
- Image information
- Distort filters are unavailable
- About color
- Color and monochrome adjustments using channels
- Choose colors in the Color and Swatches panels
- Sample
- Color mode or Image mode
- Color cast
- Add a conditional mode change to an action
- Add swatches from HTML CSS and SVG
- Bit depth and preferences
- Layers
- Layer basics
- Nondestructive editing
- Create and manage layers and groups
- Select, group, and link layers
- Place images into frames
- Layer opacity and blending
- Mask layers
- Apply Smart Filters
- Layer comps
- Move, stack, and lock layers
- Mask layers with vector masks
- Manage layers and groups
- Layer effects and styles
- Edit layer masks
- Extract assets
- Reveal layers with clipping masks
- Generate image assets from layers
- Work with Smart Objects
- Blending modes
- Combine multiple images into a group portrait
- Combine images with Auto-Blend Layers
- Align and distribute layers
- Copy CSS from layers
- Load selections from a layer or layer mask's boundaries
- Knockout to reveal content from other layers
- Selections
- Get started with selections
- Make selections in your composite
- Select and Mask workspace
- Select with the marquee tools
- Select with the lasso tools
- Adjust pixel selections
- Move, copy, and delete selected pixels
- Create a temporary quick mask
- Select a color range in an image
- Convert between paths and selection borders
- Channel basics
- Save selections and alpha channel masks
- Select the image areas in focus
- Duplicate, split, and merge channels
- Channel calculations
- Get started with selections
- Image adjustments
- Replace object colors
- Perspective warp
- Reduce camera shake blurring
- Healing brush examples
- Export color lookup tables
- Adjust image sharpness and blur
- Understand color adjustments
- Apply a Brightness/Contrast adjustment
- Adjust shadow and highlight detail
- Levels adjustment
- Adjust hue and saturation
- Adjust vibrance
- Adjust color saturation in image areas
- Make quick tonal adjustments
- Apply special color effects to images
- Enhance your image with color balance adjustments
- High dynamic range images
- View histograms and pixel values
- Match colors in your image
- Crop and straighten photos
- Convert a color image to black and white
- Adjustment and fill layers
- Curves adjustment
- Blending modes
- Target images for press
- Adjust color and tone with Levels and Curves eyedroppers
- Adjust HDR exposure and toning
- Dodge or burn image areas
- Make selective color adjustments
- Image repair and restoration
- Image enhancement and transformation
- Drawing and painting
- Paint symmetrical patterns
- Draw rectangles and modify stroke options
- About drawing
- Draw and edit shapes
- Create star or any other pointed shape
- Painting tools
- Create and modify brushes
- Blending modes
- Add color to paths
- Edit paths
- Paint with the Mixer Brush
- Brush presets
- Gradients
- Gradient interpolation
- Fill and stroke selections, layers, and paths
- Draw with the Pen tools
- Create patterns
- Generate a pattern using the Pattern Maker
- Manage paths
- Manage pattern libraries and presets
- Draw or paint with a graphics tablet
- Create textured brushes
- Add dynamic elements to brushes
- Gradient
- Paint stylized strokes with the Art History Brush
- Paint with a pattern
- Sync presets on multiple devices
- Migrate presets, actions, and settings
- Text
- Filters and effects
- Saving and exporting
- Color Management
- Web, screen, and app design
- Video and animation
- Printing
- Automation
- Troubleshooting
Curves overview
In the Curves adjustment, you adjust points throughout an image’s tonal range. Initially, the image’s tonality is represented as a straight diagonal line on a graph. When adjusting an RGB image, the upper-right area of the graph represents the highlights and the lower-left area represents the shadows. The horizontal axis of the graph represents the input levels (original image values) and the vertical axis represents the output levels (new adjusted values). As you add control points to the line and move them, the shape of the curve changes, reflecting your image adjustments. The steeper sections of the curve represent areas of higher contrast while flatter sections represent areas of lower contrast.
You can save Curves adjustment settings as presets. See Save adjustment settings and Reapply adjustment settings.
The Curves adjustment can also be applied to CMYK, LAB, or Grayscale images. For CMYK images, the graph displays percentages of ink/pigment. For LAB and Grayscale images, the graph displays light values.
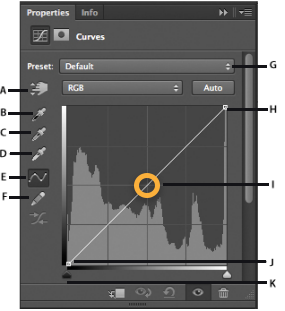
A. On-image adjustment tool B. Sample in image to set black point. C. Sample in image to set gray point. D. Sample in image to set white point. E. Edit points to modify the curve. F. Draw to modify the curve. G. Curves presets menu H. Set black point. I. Set gray point. J. Set white point. K. Show clipping.

Adjust image color and tone with Curves
Moving a point in the top portion of the curve adjusts the highlights. Moving a point in the center of the curve adjusts the midtones, and moving a point in the bottom section of the curve adjusts the shadows. To darken highlights, move a point near the top of the curve downward. Moving a point either down or to the right maps the Input value to a lower Output value, and the image darkens. To lighten the shadows, move a point near the bottom of the curve upward. Moving a point either up or to the left maps a lower Input value to a higher Output value, and the image lightens.
-
- Click the Curves icon
 in the Adjustments panel.
in the Adjustments panel. - Choose Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Curves. Click OK in the New Layer dialog box.
NoteChoosing Image > Adjustments > Curves applies the adjustment directly to the image layer and discards image information.
- Click the Curves icon
-
(Optional) To adjust the color balance, in the Properties panel, choose the channel you want to adjust from the menu to the left of the Auto button.
-
In the Properties panel, do any of the following:
- Click directly on the curve line and then drag the control point to adjust a tonal area.
- Select the On-image adjustment tool and then drag in the area of the image you want to adjust.
- Select the On-image adjustment tool and click the tonal areas in the image that you want to adjust. This places control points along the curve line.
- Choose a preset from the Preset menu.
Dragging a control point up or down lightens or darkens the tonal area you’re adjusting. Dragging a control point left or right increases or decreases the contrast. You can add up to 14 control points to the curve. To remove a control point, drag it off the graph. As you adjust the tonality, the graph continues displaying the original diagonal baseline and image histogram as references. These options can be turned off, see Set Curves Display Options.
-
(Optional) Do any of the following to modify the adjustment:
- Add more points directly to the curve to adjust different tonal areas.
- Click the On-image adjustment tool in other areas of the image, and drag up or down.
- Move the Set Black and White Point sliders or use the Eyedropper tools to specify the darkest and lightest values in the image.
- Click a point on the curve, and enter values in the Input and Output text boxes.
- Select the pencil icon and draw a new curve over the existing one. When you have finished, click the Smooth the Curve Values icon or to smooth the curve you drew. Clicking more than once continues to smooth the curve further.
Points on the curve remain anchored until you move them. You can make an adjustment in one tonal area without affecting other areas.


Removing control points from a curve
To remove a control point, do any of the following:
- Drag the control point off the graph.
- Select the control point and press Delete.
- Ctrl-click (Windows) or Command-click (Mac OS) the control point.
Set Curve display options
You can control the curve grid display using the Curve display options.
-
Apply a Curves adjustment.
-
In the Properties panel, choose Curves Display Options from the panel menu.
NoteIf you chose Image > Adjustments > Curves, expand the Curve Display Options in the Curves dialog box.
-
In the Curves Display Options dialog box, select any of the following:
Light (0-255) Displays the intensity values for RGB images in a range from 0 to 255, with black (0) at the lower-left corner.
Pigment/Ink % Displays the percentages for CMYK images are displayed in a range from 0 to 100, with highlights (0%) at the lower-left corner.
Simple Grid Displays gridlines in 25% increments.
Detailed Grid Displays gridlines in 10% increments.
Show Channel Overlays Displays color channel curves superimposed on the composite curve.
Histogram Displays a histogram of the original image tonal values behind the graph.
Baseline Displays the original image color and tonality as a 45-degree angle line for reference,
Intersection Line Displays horizontal and vertical lines to help you align control points as your drag them relative to the histogram or grid.NoteTo change the gridline increment, Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac OS) the grid.
Apply an Auto correction in Curves
-
Click Auto in the Properties panel.
Auto applies an automatic color correction using the current default setting. To change the default setting, choose Auto Options from the Properties panel menu and set the options in the Auto Color Correction Options dialog box. You can apply an Auto Color, Auto Contrast, or Auto Tone correction to an image. For more information on these options, see Set Auto adjustment options.
Set black and white points using the black point and white point sliders
When applying a Curves adjustment, use the black and white sliders to quickly set the black and white points (pure black and pure white values) in the image.
-
Drag the black and white point sliders to any point along the horizontal axis. Note that the Input value changes as your drag.
-
To preview clipping as you adjust black and white points, do one of the following:
- Hold down Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac OS).
- Choose Show Clipping For Black/White Points from the panel menu.
Add contrast to the midtones of a photo with Curves
If
the image uses the full tonal range, but needs midtone contrast,
Click the Curves icon ![]() in
the Adjustments panel. Drag the curve into an S shape.
in
the Adjustments panel. Drag the curve into an S shape.


Keyboard shortcuts: Curves
You can use these keyboard shortcuts for Curves:
- To set a point on the curve for the selected color in each color component channel (but not in the composite channel), Shift+Ctrl-click (Windows) or Shift+Command-click (Mac OS) in the image.
- To select multiple points, Shift-click points on the curve. Selected points are filled with black.
- To deselect all points on the curve, click in the grid, or press Ctrl‑D (Windows) or Command-D (Mac OS).
- To select the next higher point on the curve, press the plus key; to select the next lowest, press the minus key.
- To move selected points on the curve, press the arrow keys.
(Curves dialog box) To set a point on the curve for the current channel, Ctrl-click (Windows) or Command-click (Mac OS) in the image.
If you’re instead using the Curves adjustment, simply click in the image with the On-image adjustment tool ![]() .
.