Cache Strategy
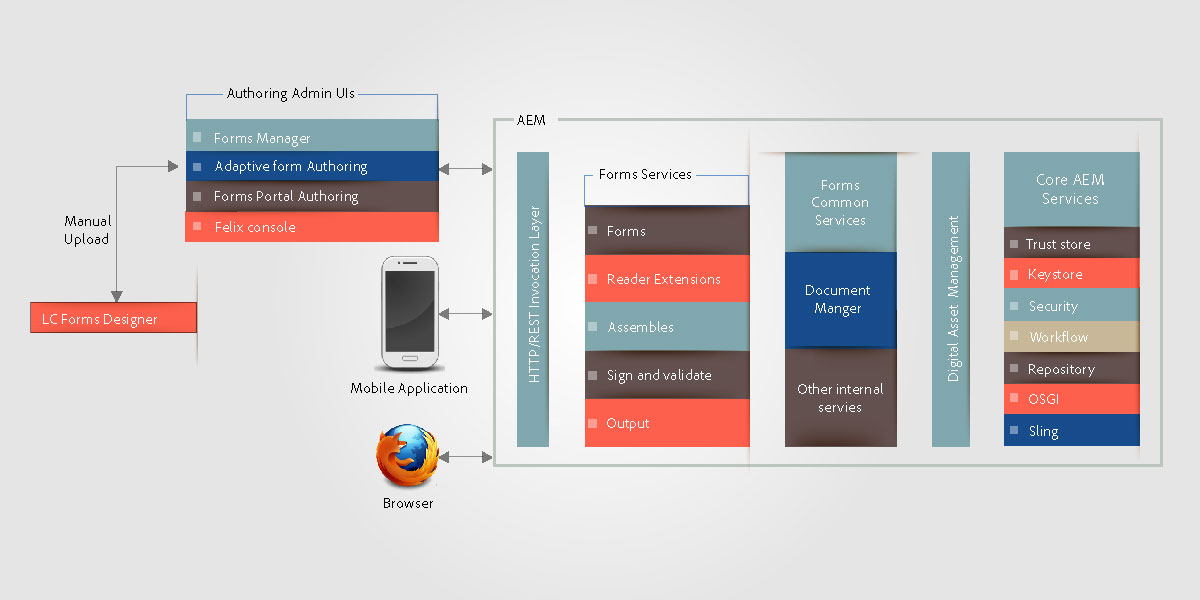
Mobile Forms is deployed as a package within the embedded CQ instance and exposes Mobile Forms functionality as REST end point over HTTP/S using RESTful Apache Sling Architecture.
Apache Sling is resource-centric. It uses a request URL to first resolve the resource. Each resource has a sling:resourceType (or sling:resourceSuperType) property. Based on this property, the request method, and properties of the request URL, a sling script is then selected to handle the request. This sling script can be a JSP or a servlet. For Mobile Forms, Profile nodes act as sling resources and Profile Renderer acts as the sling script that handles the request to render the mobile form with a particular profile. A Profile Renderer is a JSP that reads parameters from a request and calls the Forms OSGi Service.
For details on REST endpoint and supported request parameters, see Rendering Form Template.
When a user makes a request from a client device such as an iOS or Android browser, Sling first resolves the Profile Node based on the request URL. From this Profile Node, it reads sling:resourceSuperType and sling:resourceType to determine all available scripts that can handle this Form Render request. It then uses Sling request selectors along with request method to identify the script best suited for handling this request. Once the request reaches a Profile Renderer JSP, the JSP calls the Forms OSGi service.
For more details on sling script resolution, see AEM Sling Cheat Sheet or Apache Sling Url decomposition.
Mobile Forms cache all the intermediate objects required to process (rendition or submission) a form on the first request. It does not cache the objects dependent on the data as such objects are likely to change.
Mobile Form maintains two different levels of cache, PreRender cache and Render Cache. The preRender cache contains all the fragments and images of a resolved template and Render cache contains rendered content such as HTML.


Mobile Forms do not cache templates that have missing references of fragments and images. If Mobile Forms take more than normal amount of time, then check the server logs for missing references and warnings. Also ensure that the maximum size of the object is not reached.
Forms OSGi service processes a request in two steps:
A form to be rendered can reside in LiveCycle repository. If there is any update in form or any of assets used inside form, the form cache component detects it and the cache for that particular form is invalidated. Once the Forms OSGi service completes processing, the Profile Renderer jsp adds JavaScript library references and styling to this form and returns the response to client. A typical web server like Apache can be used here with HTML compression on. A web server would reduce the response size, network traffic, and time required to stream the data between server and client machine significantly.
When a user submits the form, the browser sends state of form in JSON format to the submit service proxy; then the submit service proxy generates a data XML using JSON data and submits that data XML to submit endpoint.
Mobile Forms is delivered as a CQ package that can be managed from the CQ Package Manager available at http://:/lc/crx/packmgr/index.jsp.
adobe-lc-forms-pkg.zip: This package is the main single install package. This package contains the following subpackages and bundles:
Adobe XFA Forms Renderer (com.adobe.livecycle.adobe-lc-forms-core) is the display name of the Mobile Forms OSGi bundle when viewed from Bundle View of Felix admin console (http://<host>:<port>/lc/system/console/bundles).
This component contains OSGi components for render, cache management, and configuration settings.
This OSGi Service contains the logic to render an XDP as HTML and handles the submission of a form to generate data XML. This service uses LiveCycle Forms service container. The Forms service container internally calls native component XMLFormService.exe that performs the processing.
If a render request is received, this component calls Forms service container to generate layout and state information that is further processed to generate HTML and JSON form DOM states.
This component is also responsible for generating data XML from submitted form state JSON.
The caching mechanism described in this article is updated for LiveCycle ES4 Service Pack 1. If you are on the LiveCycle ES4 base release, follow the steps described in Key Distinctions between LiveCycle ES4 and Service pack 1.
Mobile Forms uses caching to optimize throughput and response time. You can configure the level of the cache service to fine-tune the trade-off between performance and space utilization.
|
Cache Strategy |
Description |
|
None |
Do not cache artifacts |
|
Conservative |
Cache only intermediate artifacts that are generated before the render of the form like template containing inline fragments and images |
|
Aggressive |
Cache Rendered HTML content |
Mobile Forms perform in-memory caching using LRU strategy. If cache strategy is set to None, cache is not created. LRU eviction policy is based on number of forms. You can also specify the threshold size beyond which objects are not cached.
In-memory cache is not shared between cluster nodes.
Configuration Service enables tuning the configuration parameters and cache settings for Mobile Forms.
To update these settings, go to the CQ Felix Admin Console (available at http://<server>:<port>/lc/system/console/configMgr), search for and select LC Forms Configuration.
You can configure the cache size or disable the cache using configuration service. For detailed information, see Cache Component. You can also enable debugging using Debug Options parameter. More information about debugging forms can be found at Debugging Mobile Forms.
The Runtime Package contains the client-side libraries used to render HTML forms.
Important components available as part of Runtime package:
Adobe XFA implementation supports two kinds of scripting languages to enable user-defined logic execution in forms: JavaScript and FormCalc.
The scripting engine of HTML Forms is written in JavaScript to support the XFA scripting API in both these languages.
At render time, the FormCalc script is translated (and cached) into JavaScript on the server transparent to the user or designer.
This scripting engine uses some of the feature of ECMAScript5 like Object.defineProperty. The engine / library is delivered as CQ Client Lib with the category name xfaforms.profile. It also provides FormBridge API to enable external portals or apps to interact with form. Using FormBridge, an external app can programmatically hide certain elements, get or set their values, or change their attributes.
For more details, see the Form Bridge article.
The layout and visual aspect of the Mobile Forms is based on SVG 1.1, jQuery, BackBone, and CSS3 features. The initial appearance of a form is generated and cached at server. The tweaking of that initial layout and any further incremental changes to the form layout are managed on the client. To achieve this, the Runtime package contains a layout engine written in JavaScript and based on jQuery/Backbone. This engine handles all dynamic behavior, like Add/Remove repeatable instances, Growable object layout. This layout engine renders a form one page at a time. Initially a user views only one page and the horizontal scroll bar accounts for only first page. However, when a user scrolls down, the next page starts rendering. This page-by-page rendition reduces the amount of time required to render the first page in a browser and enhances the perceived performance of the form. This engine/library is part of CQ Client Lib with the category name xfaforms.profile.
Layout Engine also contains a set of widgets used to capture the value of form fields from a user. These widgets are modeled as jQuery UI Widgets that implement certain additional contract to work seamlessly with Layout engine.
For more details on widgets and the corresponding contracts, see Custom Widgets for Mobile Forms.
The style associated with the HTML elements is added either inline or based on embedded CSS block. Some common styles which are not dependent on form are part of CQ Client Lib with category name xfaforms.profile.
In addition to default styling properties, each form element also contains certain CSS classes based on element type, name, and other properties. Using these classes, one can restyle elements by specifying their own CSS.
For more details on default styling and classes, see Introduction to styles.
Any scripts that are marked to run-at-server or marked to call a Web Service (regardless of where it is marked to execute) always executes on server.
The client script engine:
By default, Mobile Forms is supported in English, French, German, and Japanese language. Based on the locale received in the request header, corresponding Resource Bundle is sent to the client. This resource bundle is added to Profile JSP as a CQ Client Lib with category name xfaforms.I18N. You can override the logic of picking up the locale package in the profile.
Sling package contains content related to Profiles and Profile Renderer.
Profiles are the Resource nodes in sling that represent a form or Family of Forms. At the CQ Level, these profiles are JCR nodes. The nodes reside under the /content folder in JCR repository and can be inside any sub folder under the /content folder.
The Profile node has a property sling:resourceSuperType with value xfaforms/profile. This property internally sends forward requests to the sling script for Profile nodes located in the /libs/xfaforms/profile folder. These scripts are JSP pages, that are containers for putting together the HTML forms and required JS/CSS artifacts. The pages include references to: