Traditionally, an array is a tabular structure used to hold data, much like a spreadsheet table with clearly defined limits and dimensions.
In ColdFusion, you typically use arrays to temporarily store data. For example, if your site lets users order goods online, you can store their shopping cart contents in an array. Using an array lets you make changes easily without committing the information, which the user can change before completing the transaction, to a database.
Basic array concepts
Subsequent discussions of ColdFusion arrays are based on the following terms:
- Array dimension The relative complexity of the array structure.
- Index The position of an element in a dimension, ordinarily surrounded by brackets: my1Darray1, my2Darray11, my3Darray111.
- Array element: Data stored at an array index. The simplest array is a one-dimensional array, like a row in a table. A one-dimensional array has a name (the variable name) and a numeric index. The index number references a single entry, or cell, in the array.
Thus, the following statement sets the value of the fifth entry in the one-dimensional array MyArray to "Robert":
<cfset MyArray[5] = "Robert">
A basic two-dimensional (2D) array is like a simple table. A three-dimensional (3D) array is like a cube of data, and so on. ColdFusion lets you directly create arrays with up to three dimensions. You can use multiple statements to create arrays with more than three dimensions.
The syntax my2darray13="Paul" is the same as saying "My2dArray is a two-dimensional array and the value of the array element index 13 is Paul".
About ColdFusion arrays
ColdFusion arrays differ from traditional arrays, because they are dynamic. For example, in a conventional array, array size is constant and symmetrical, whereas in a ColdFusion array, you can have rows of differing lengths based on the data that is added or removed.
A conventional 2D array is like a fixed-size table made up of individual cells.
A ColdFusion 2D array is actually a one-dimensional array that contains a series of additional 1D arrays. Each of the arrays that make up a row can expand and contract independently of any other column.
The following figure represents a ColdFusion 2D array:
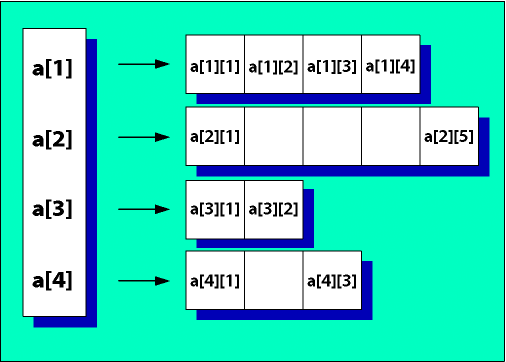

A ColdFusion 3D array is essentially three nested sets of 1D arrays. The differences between traditional and ColdFusion 3D arrays are similar, but much harder to show on a page.
Dynamic arrays expand to accept data that you add to them and contract as you remove data from them.
Negative indices
You can use negative indices to get the elements of an array. For example, if an array, arr, has n elements, then:
- arr[-1] returns a[n]
- arr[-2] returns a[n-1]
- ...and so on
For example,
<cfscript>
animals = ['cat', 'dog', 'fish', 'bison'];
writeOutput(animals[-1]); //gets the last element
writeOutput(animals[-2]); //gets the last but one element
</cfscript>
You can also use negative indices on multi-dimensional arrays. For example,
<cfscript> arr = ArrayNew(2); // Build first album array, Surfin' Safari arr[1][1] = "Surfin' Safari"; arr[1][2] = "County Fair"; arr[1][3] = "Ten Little Indians"; // Build second album array, Surfin' USA arr[2][1] = "Surfin' USA"; arr[2][2] = "Farmer's Daughter"; arr[2][3] = "Miserlou"; // Build third album array, Surfer Girl arr[3][1] = "Surfer Girl"; arr[3][2] = "Catch a Wave"; arr[3][3] = "The Surfer Moon"; writeDump(arr) writedump(arr[-1]) writedump(arr[-1][1]) // Surfer Girl writedump(arr[-1][2]) // Catch a Wave writedump(arr[-1][3]) // The Surfer Moon writedump(arr[-1][-1]) // The Surfer Moon writedump(arr[-1][-2]) // Catch a Wave writedump(arr[-1][-3]) // Surfer Girl writedump(arr[-3]) </cfscript>